Table of Contents
SKB Knowledge
| Reference | SKB API(Chinese) |
SKB Notes
| len | the size of a complete input packet including headers. This value includes data in the kmalloc'd part, fragment chain and/or unmapped page buffers. | |
|---|---|---|
| data_len | the number of bytes in the fragment chain and in unmapped page buffers and is normally 0. skb→data_len = struct skb_shared_info→frags[0…struct skb_shared_info→nr_frags].size + size of data in struct skb_shared_info→frag_list | |
| truesize | skb→truesize = skb→len + sizeof(struct sk_buff) | |
| users for sk_buff only | share skb and its data buffer skb_get increase it by 1. kfree_skb reduce it by 1, if it becomes 0, then free it | skb_shared |
| cloned for skb→data and its skb_shared_info | different skb but with same data buffer | skb_cloned |
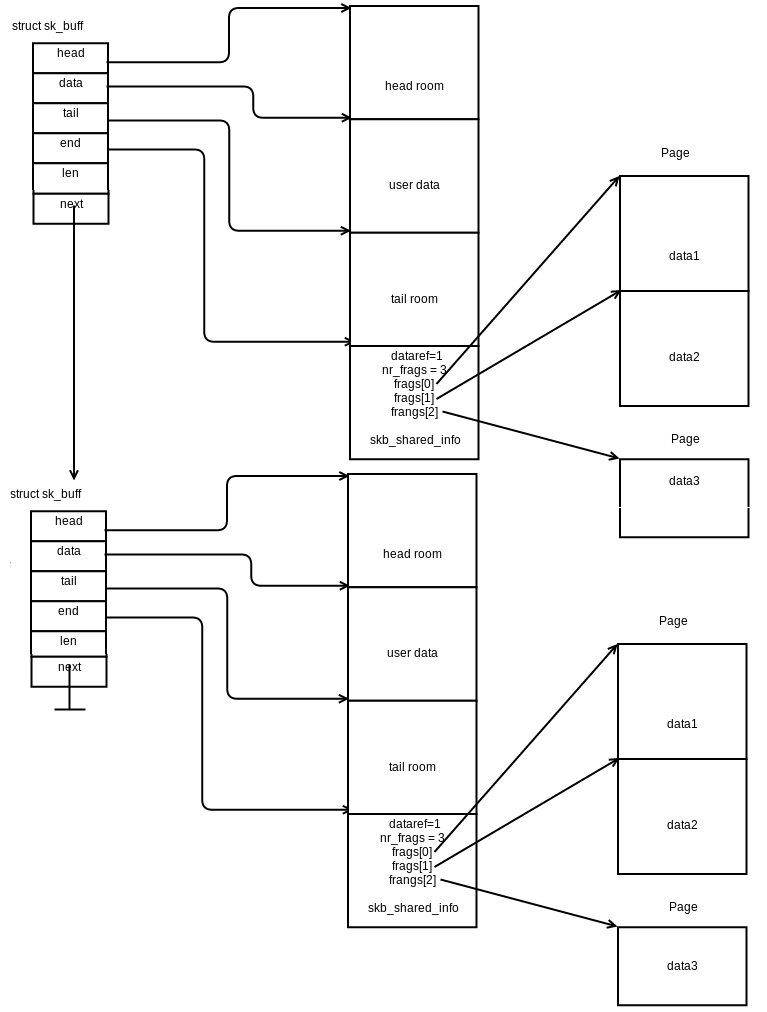
| skb_shared_info | used when the data component of a single sk_buff consists of multiple fragments |
| gso_size | Warning: this field is not always filled in (UFO)! |
| gso_segs | |
| gso_type | |
| struct sk_buff *frag_list | it is for ip fragments |
| hwtstamps | |
| dataref | The number of users of the data of this sk_buff. This value is incremented each time a buffer is cloned. |
| nr_frags | used for unmapped page buffers. The number of elements of frags array in use. |
| frags[MAX_SKB_FRAGS] | used for unmapped page buffers, it is for scatter-gather i/o buffers |
| skb_clone | only copy skb_buff, not data and share info | increase skb→dataref by 1 |
| pskb_copy | copy skb_buff and data both, but not share info. If it needs to modify data, then need pskb_copy | increase page reference if (skb_shinfo(skb)→nr_frags) increase frag_list's user counter if (skb_has_frag_list(skb)) |
frags vs frag_list
frags[] are for scatter-gather i/o buffers frag_list is for IP fragments
- skb_shinfo(head)→frags[]
If your NIC supports SG I/O __ip_append_data will copy user space data to skb_shinfo(head)→frags, otherwise this function will make a list of skbs filled with the userspace data and all the skbs will be queued in sk→sk_write_queue.
- skb_shinfo(head)→frag_list
This member is used by IP fragments. Check ip_push_pending_frames()→ip_finish_skb() for populating the frag_list with skbs which queued in sk→sk_write_queue and check ip_fragment() for processing the frag_list.
SKB Layout
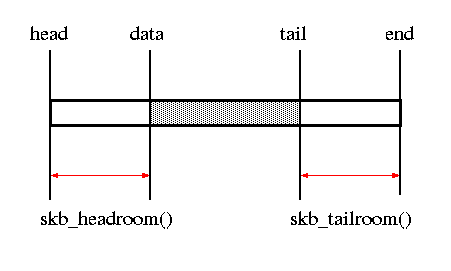
skb_headroom(), skb_tailroom()
Prototype / Description:
| int skb_headroom(const struct sk_buff *skb); | bytes at buffer head |
| int skb_tailroom(const struct sk_buff *skb); | bytes at buffer |
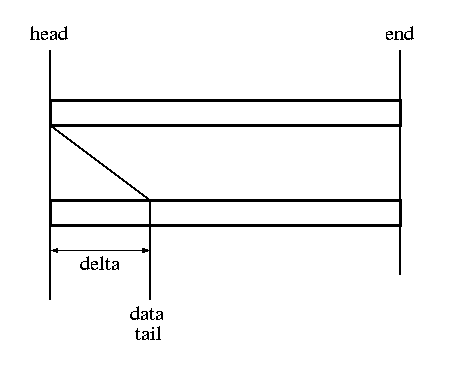
skb_reserve()
Prototype / Description:
| void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len); | adjust headroom skb→data += len; skb→tail += len; |
| linear/non-paged skb API | non-linear/paged skb API via skb_shared |
| skb_push | NA |
| skb_pull | pskb_pull: p means paged |
| skb_put | pskb_put |
| skb_trim | pskb_trim |
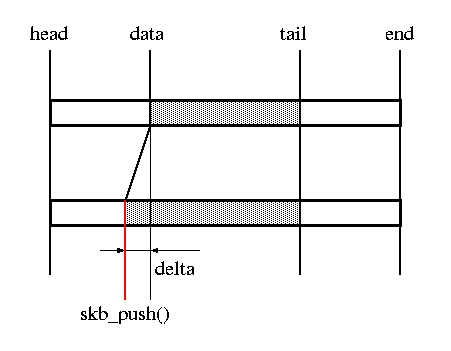
skb_push()
Prototype / Description:
| unsigned char *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len); | add data to the start of a buffer skb→data -= len; skb→len += len; |
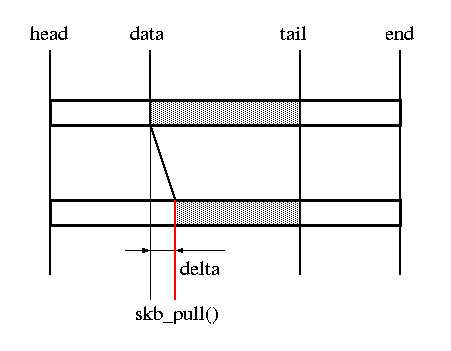
skb_pull()
Prototype / Description:
| unsigned char *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len); | remove data from the start of a buffer skb→len -= len; skb→data += len; |
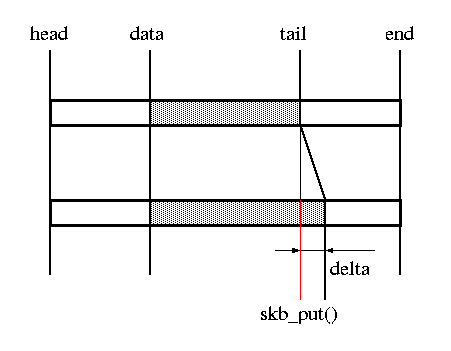
skb_put()
Prototype / Description:
| unsigned char *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len); | add data to a buffer skb→tail += len; skb→len += len; |
skb_trim()
Prototype / Description:
| void skb_trim(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len); | remove end from a buffer skb→len -= len; skb→tail = skb→data + offset |
skb destructor
Note: skb→destructor will be used by linux network stack itself without checking whether it is NULL or not.
When a received packet is to be charged to a socket, we invoke the function 'skb_set_owner_r'. It sets 'skb→sk' to the socket, hooks up a destructor function, and accounts the data bytes in 'sk→sk_rmem_alloc'. Often, this function is invoked by the helper routine 'skb_queue_rcv_skb'.
static inline void skb_set_owner_r(struct sk_buff *skb, struct sock *sk)
{
skb->sk = sk;
skb->destructor = sock_rfree;
atomic_add(skb->truesize, &sk->sk_rmem_alloc);
}
Later when the packet is freed up (via 'kfree_skb()', usually after the receive packet data is copied into user space), the destructor is invoked. In the above example, the destructor is 'sock_rfree()'. It releases the buffer allocate space from 'sk→sk_rmem_alloc'.
void sock_rfree(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct sock *sk = skb->sk;
atomic_sub(skb->truesize, &sk->sk_rmem_alloc);
}
On the packet send side, similar things happen. Except that in the destructor we have to wake up any processes waiting for send buffer space to become available. The routines used here are 'skb_set_owner_w()' and 'sock_wfree()'.
static inline void skb_set_owner_w(struct sk_buff *skb, struct sock *sk)
{
sock_hold(sk);
skb->sk = sk;
skb->destructor = sock_wfree;
atomic_add(skb->truesize, &sk->sk_wmem_alloc);
}
...
void sock_wfree(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct sock *sk = skb->sk;
/* In case it might be waiting for more memory. */
atomic_sub(skb->truesize, &sk->sk_wmem_alloc);
if (!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_USE_WRITE_QUEUE))
sk->sk_write_space(sk);
sock_put(sk);
}
other skb APIs
- skb_orphan(): 使SKB不属于任何传输控制块。
- skb→destructor(skb);
- skb→destructor = NULL;
- skb→sk = NULL;
- skb_cow(): 确保SKB存在指定的headroom空间。如果不足,会重新分配。
- skb_cow - copy header of skb when it is required, iek, if the skb passed lacks sufficient headroom or its data part is shared, data is reallocated. If reallocation fails, an error is returned and original skb is not changed.
- skb_condense(): try to get rid of fragments/frag_list if possible. Can be used to save memory before skb is added to a busy queue. If packet has bytes in frags and enough tail room in skb→head, pull all of them, so that we can free the frags right now and adjust truesize.