Table of Contents
Private Chef from Nov-Dec, 2025
Orientation
GUIDELINES ON GOOD PERSONAL HYGIENE
- .Washing of hands
- .Short and clean finger nails.
- .Clean aprons and tidy clothes
- .Clean and tidy hair
- .Usage of hair caps or hair nets
- .Proper way of sneezing or coughing
- .Usage of waterproof plaster to cover sore or cuts
- .Usage of gloves
- .Do not handle or prepare food, or rather see a doctor if you have diarrhea, fever or illness
PREPARATION OF FOOD AND DRINKS
- .Do not prepare food and keep it at room temperature for long period before sale or consumption
- .Use only potable water for preparation of food
- .Use only food-grade ice for drinks
- .Get supplies from licensed or approved sources
- .Ensure ingredients are fresh
- .Do not use spoilt, expired, stale or contaminated ingredients
- .Clean and wash ingredients thoroughly
DISPLAY, STORAGE ANDPACKAGING OF FOOD
- .Display of food:
- - Cover food
- - Display food in showcase with sneeze guards
- Storage of hot food:
- - Hot food in proper warming or heating equipment
- - Food warmer should be 60ºC and above
- - Practice tidy way of storing food
NEA RECOMMENDED TEMPERATURES FOR STORAGE OF FOOD
| Types of Food | Temperature |
| Frozen meat | Not above -18ºC |
| lce-cream | Not above -2ºC |
| Chilled fresh meat/fish | 0ºC to 4ºC |
| Thawed frozen meat | 0ºC to 4ºC |
| Diary products | Not above 7ºC |
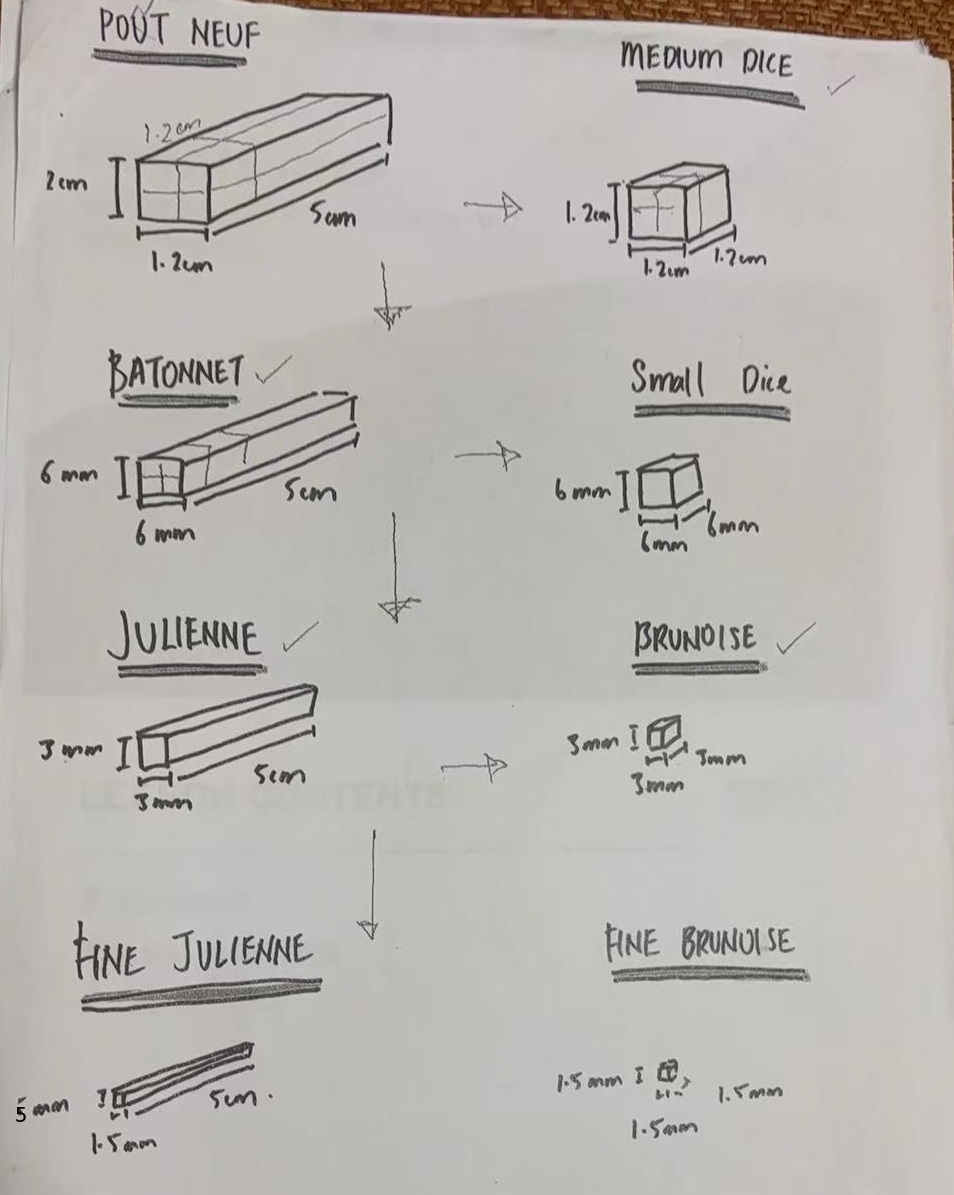
Different Cuts
Prepare Misen-Place (Value Add)
Topic 1: Basic Stocks, Soups and Sauces
Recipes & Videos
MIREPOIX (English aromatics)
- A mirepoix is a mixture of roughly chopped onions, carrots, and celery (either common pascal celery or celeriac).
- Traditionally: 2 parts onions, 1 part carrots & 1 part celery.
- Mirepoix is the flavour base for a wide variety of dishes, such as stocks, soups, stews and sauces.
米拉波瓦是法式烹饪中一种基础的芳香蔬菜混合物
Topic 2: BASIC STOCKS, SOUPS AND SAUCES
Recipe and videos
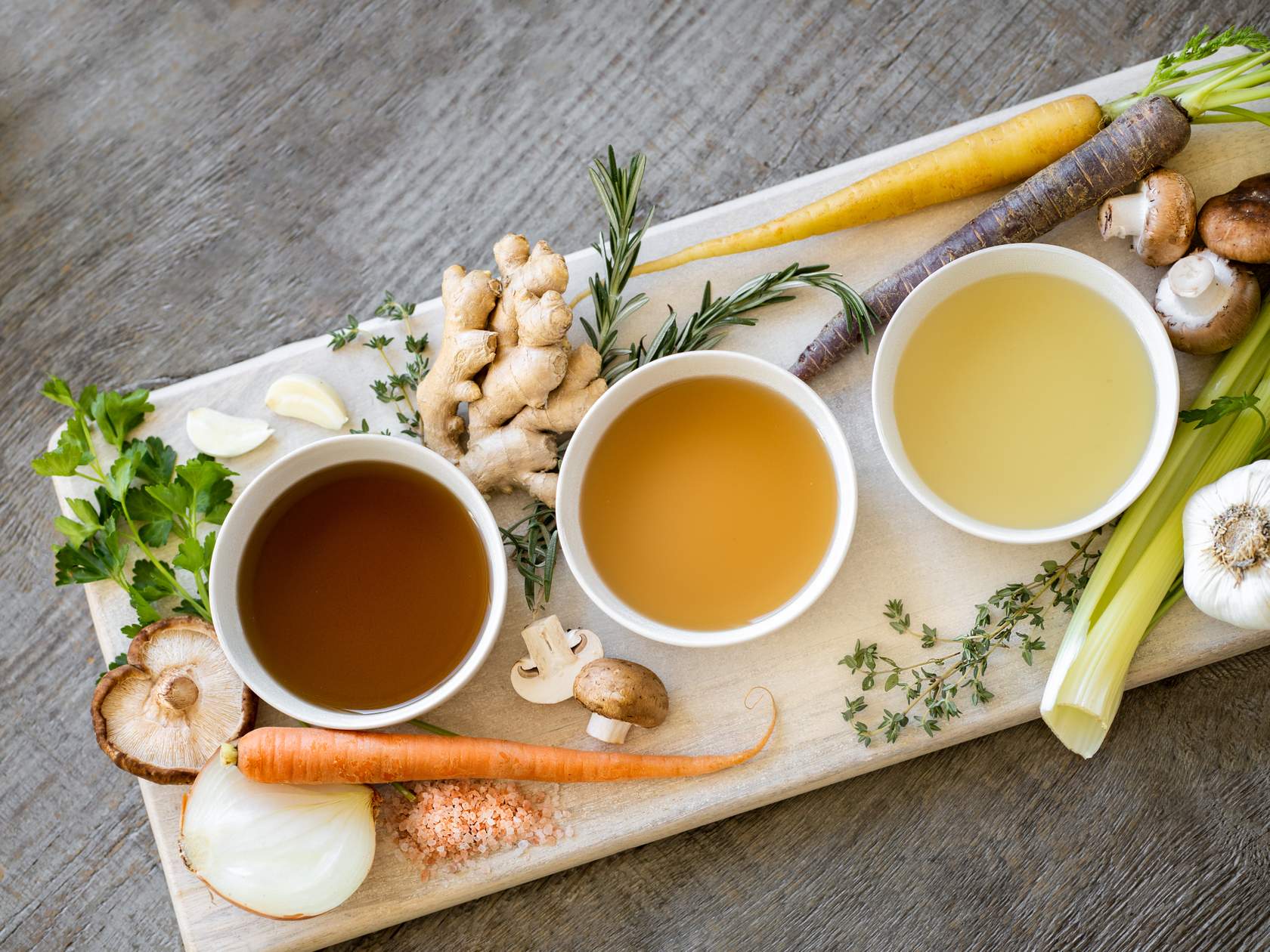
Basic Stocks
- - Are flavoured liquids
- - Key to great soups, sauces or braised dishes
- - French call a stock Fond (“Base”)
Ingredients
- - Meat bones
- - vegetable mixture (mirepoix)
- - Seasoning water
Mirepoix is a mixture of: 50% onion, 25% carrot and 25% celery
Types of stocks:
- white stock
- brown stock
- fish stock and fumet
- vegetable stock
- court-bouillon
Steps in Preparing the Stock
- 1) Start the stock in cold water.
- 2) Simmer the stock gently. Skim the stock frequently.
- 3) Strain the stock carefully.
- 4) Cool the stock quickly (food safety: to prevent food-borne illnesses or souring)
- 5) Beware of the temperature danger zone: 5-57 degree C
- 6) Store the stock properly.
- 7) Degrease the stock.
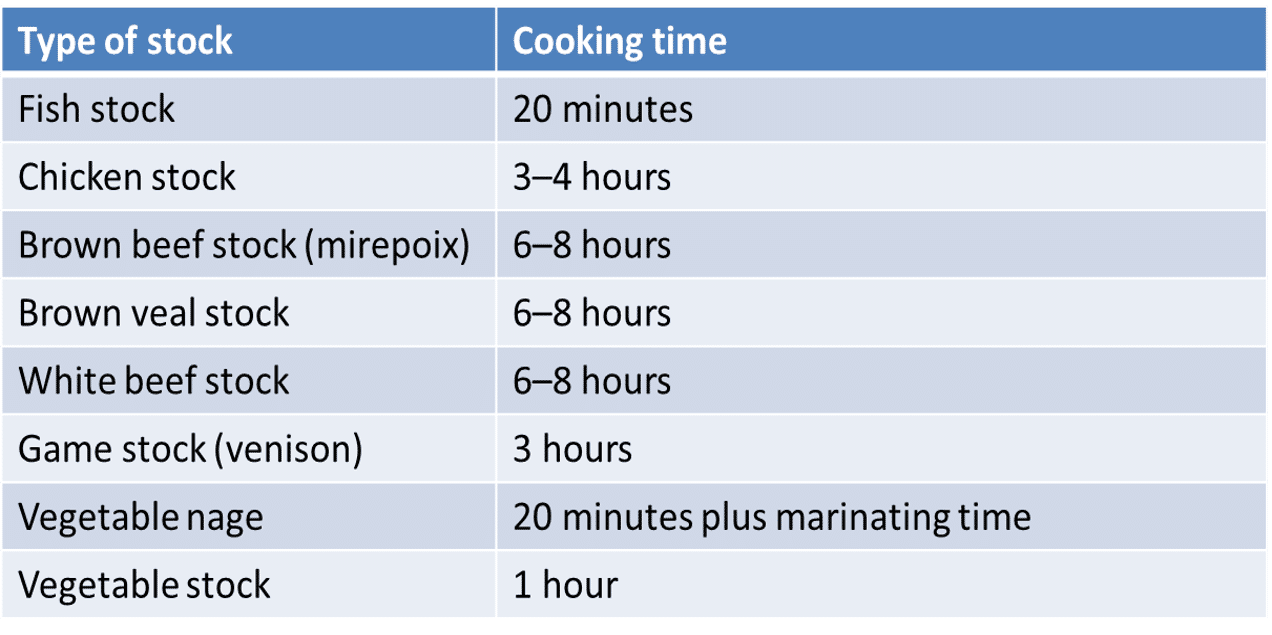
Cooking Time for Stocks
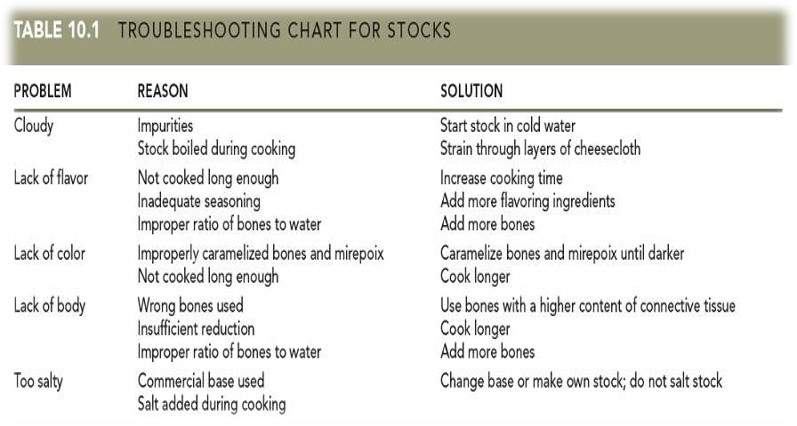
Common Faults And How to Prevent Them
Soups
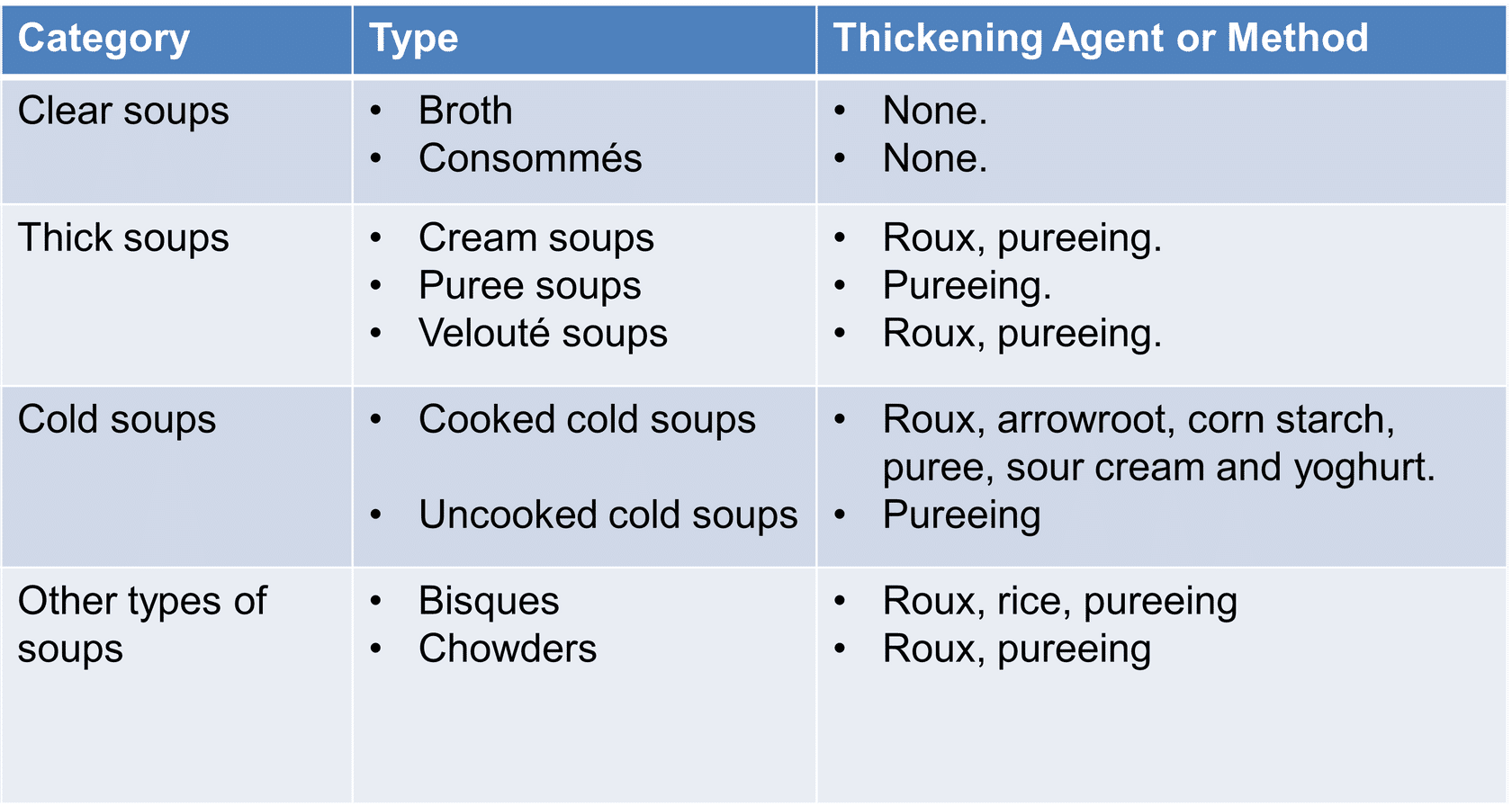
Classification of Soups
The Differences in Soups
- Clear Soups
- - All clear soups start as stock or broth.
- - Broths may be served as finished items, used as the base of other soups or refined into consommés.
- Broths
- - Made from meat, poultry, fish or vegetables cooked in a liquid.
- - Full flavored broth results when a stock and not just water is used as a liquid.
- Consommés
- - Is a stock or broth that has been clarified to remove impurities.
- - Is rich and full of flavor.
- Thick Soups
- - Includes cream soups, velouté soups and purée soups
- - Cream soups:
- - Are prepared by simmering ingredients in a white stock or in thin veloutée sauce
- - Mixture is strained. To finish, cream is added.
- - Texture is very smooth and rich
- - Example: Cream of broccoli
- - Pureed soups:
- - Are prepared in stock or water
- - Ingredients are pureed
- - Texture is slight coarse and grainy
- - Example: Split pea soup
- uncooked cold soup
- Cold soups can be as simple as a chilled version of cream soup or as creatives as a cold fruit soup blended with yoghurt.
- cooked cold soup
- Many cold soups are simply a chilled version of a hot soup for example consommé madrilène and consommé Portuguese.
Garnishes for Soups Garnishes are used to add texture, flavour & visual appearance of the dish
Common garnishes for soups are:
- Clear soups:
- - Fresh herbs
- - Diced or thinly shredded vegetables
- - Meat balls
- Cream soups:
- - Croutons
- - Cream
- - Fresh herbs
- - Crushed dried spice and herbs
- Purée soups:
- - Cream
- - Extra virgin olive oil
- - Grated cheese
- Cold Soups:
- - Sour cream
- - Whipped yoghurt
- - Fruit sauce
- - Sliced fruits or cooked vegetables
Roux - Types of Roux
Note: roux a cooked mixture of fat and flour (or other starch) used as an ingredient to thicken soups, sauces, or gravies, adding richness and body, not a final dish itself
- White roux
- Use for white sauces, e.g., béchamel where little or no colour is desired
- Blond roux
- Use in ivory-Colored sauces, e.g., veloute or where a richer flavor is desired
- Brown roux
- Use in brown sauces and dishes where a dark colour is desired
Preparing Roux
- Whether it will be white, blond or brown, the procedure for making the roux is the same.
- Use heavy bottom pan to prepare the roux. Heat clarified butter and add the flour and stir to form a paste.
- Cook the sauce on slow or medium heat until the desired colour is achieved.
- Brown roux requires much longer duration to develop its characteristics colour and aroma.
Method of Using Roux for Soups and Sauces
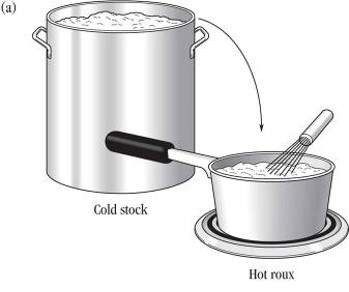
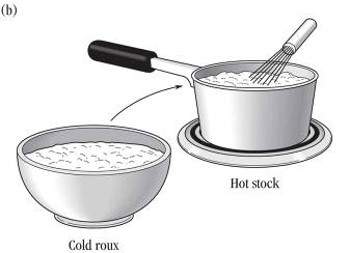
- When thickening stock with roux, either
- (a) add cold stock to hot roux, or
- (b) add cold roux to hot stock.
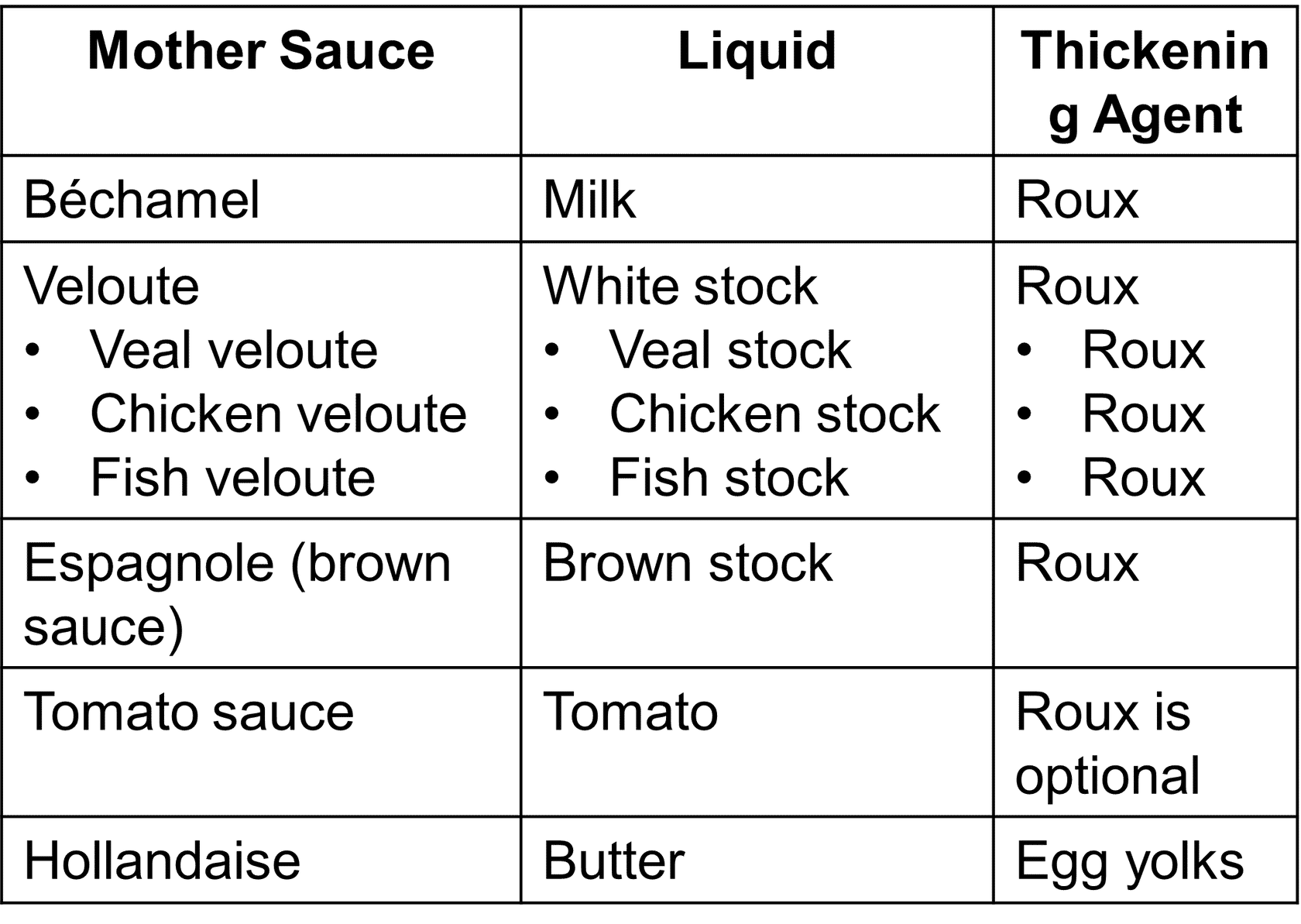
The Structure of Sauces
The Structure of Sauces - The Liquids, Thickening Agents, and Flavoring ingredients
A liquid:
- - Milk (for béchamel)
- - White stock (for veloute sauces)
- - Brown stock (for brown sauce or espagnole)
- - Tomato plus stock (for tomato sauce)
- - Clarified butter (for hollandaise)
Thickening Agents:
- - Flour
- - Cornstarch
- - Arrowroot
Flavoring ingredients:
- - Lemon juice
- - Sherry
- - Cayenne
- - White pepper
Sauce Families
- Mother or Leading sauces:
- - Distinguished by the liquids and thickening agents
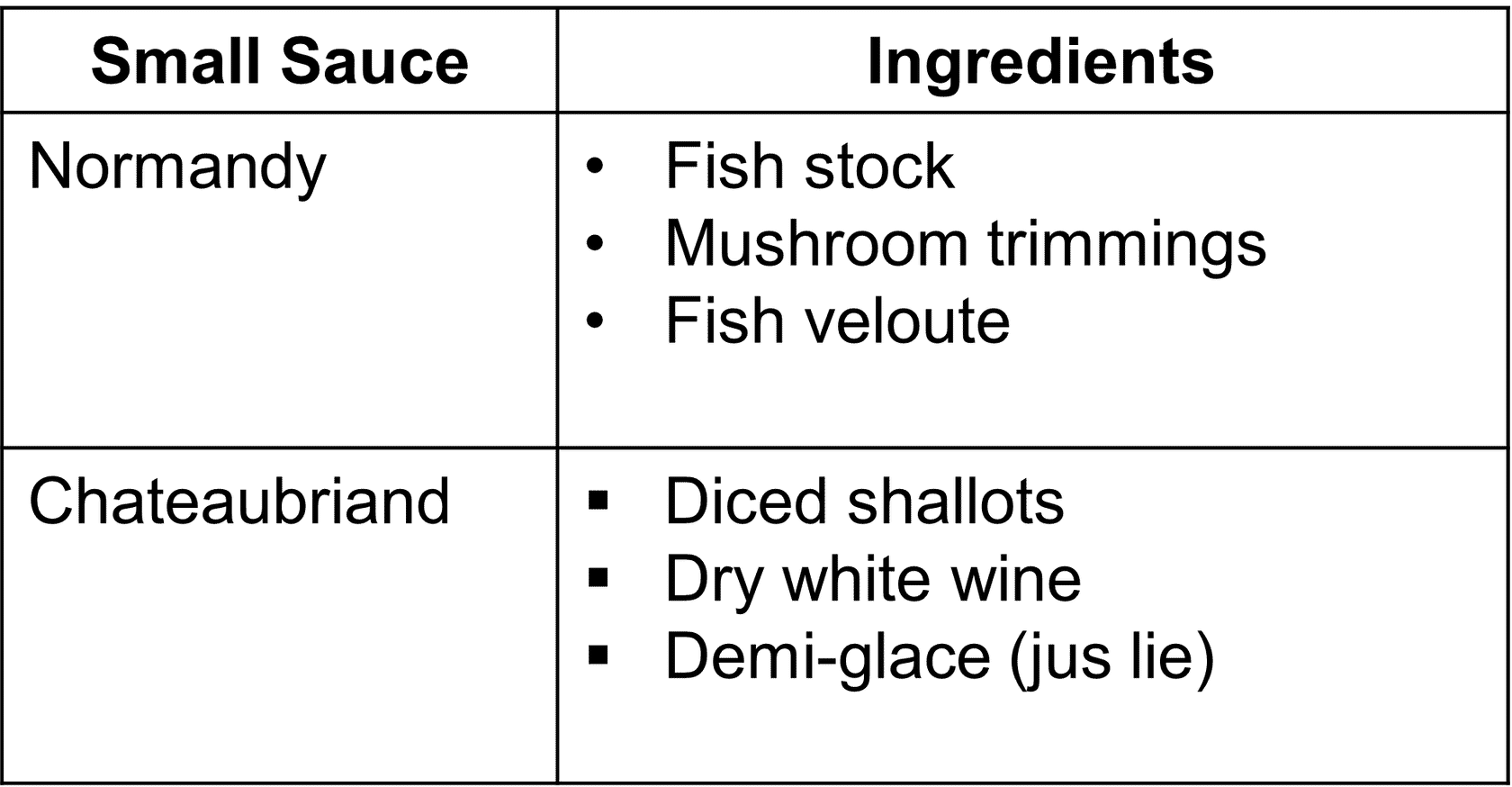
- Small or Compound sauces:
- - Are grouped into families based on their leading sauces
- - A small sauce may be named for its ingredients, place of origin or creator
The Mother Sauces
The Small Sauces (2 examples)
Safety Alert: Handling emulsified butter sauce
Examples: Hollandaise, Bearnaise, etc
To minimize the risk of food-borne illnesses:
- - Always use clean, sanitized utensils
- - Schedule sauce production as close to the time of service as possible.
- - Never hold hollandaise sauce more than one and half hours.
- - Never mix the old batch with new one.
Topic 3: French Cuisin
Recipe and videos
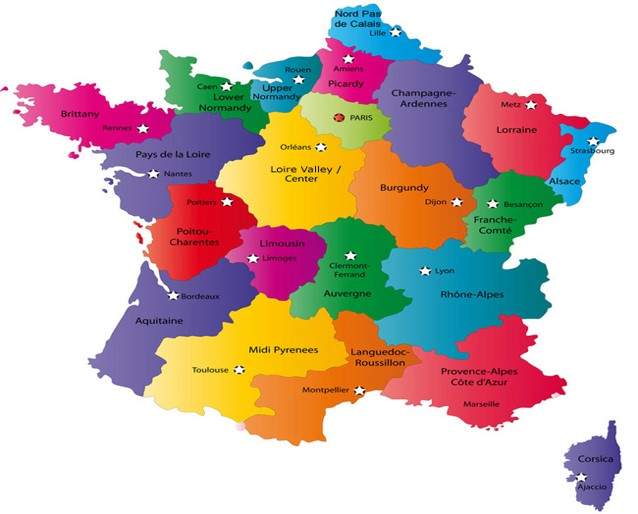
Map of France
Local Products of France
Vegetables:
- –Artichokes
- –Swiss chard
- –French peas, etc.
- –Ham
- –Cheese
- –Wine
- –Foie Gras
- –Escargot, etc.
Main Regional Cuisines :
Cuisine du Terroir - covers regional specialties with a strong focus on quality local produce Alsace:
- •Regional produces: cabbages, sausages, salted pork, potatoes
- •Regional specialty: Chou Croute Garnie
Alps:
- •Regional produces: Ham, potatoes, cream, milk and cheese
- •Regional specialty: Gratin dauphinois, Raclette
Auvergne: Tripoux (pork tripe in a tasty sauce) and Aligot (mashed potatoes blended with young tomme cheese)
Bretagne: crepes (milk, egg, flour, sugar)
Bourgogne: Boeuf Bourguignon (beef stewed in red wine)
Lorraine: Quiche Lorraine (dough, cream, egg, bacon, milk)
Cote d’Azur/Provence: Bouillabaisse (stew of mixed Mediterranean fish, tomato, herbs) and Ratatouille (dice of tomato, zucchini, eggplant, garlic, red pepper)
South West: Cassoulet (beans, sausages, duck or goose) and Foie gras (the liver of a force-fed duck or goose)
Main Regional Cuisines : Cuisine Bourgeoisie
Includes all classic French dishes, specifically regional dishes which have been adapted over the years. This type of cooking includes the rich, cream-based sauces and sometimes complex cooking techniques.
Main Regional Cuisines : Nouvelle Cuisine
Developed in the 1970’s. This type of cooking is characterized by shorter cooking times, much lighter sauces, dressings and smaller portions presented in a refined decoration.
Typical French Menu Flow
Introduction
- 1.L’ Aperitif (Aperitif)
- 2.L’ Entrée (Appetizer)
- 3.Le Plat Principal (Main course)
- 4.Le Fromage (Cheese)
- 5.Le Dessert (Dessert)
- 6.Le Cafe (Coffee)
Aperitif
- •Can be a cocktail, liqueur or fruit juices before a meal
- •Typical aperitifs:
- - Kir and Kir Royale
- - Biere (beer)
- - wine
- •Mediterranean canapé preparations:
- -Tapenade (olive based)
- -Ancholivade (anchovy based)
- -Mousse de saumon (salmon mousse)
- -Brandade de morue (cod cream)
- -Crabe au citron (crab with lemon)
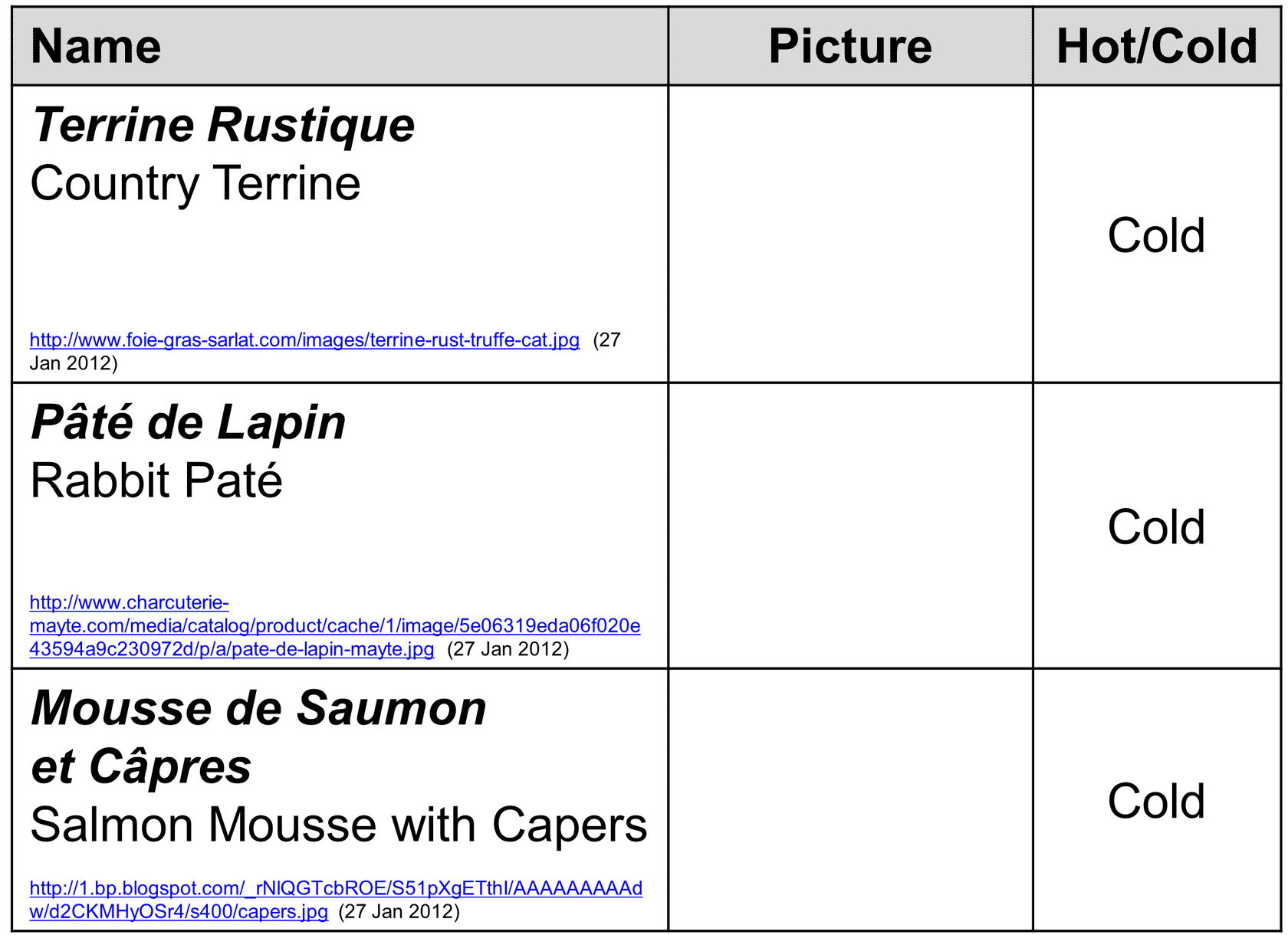
Appetizers
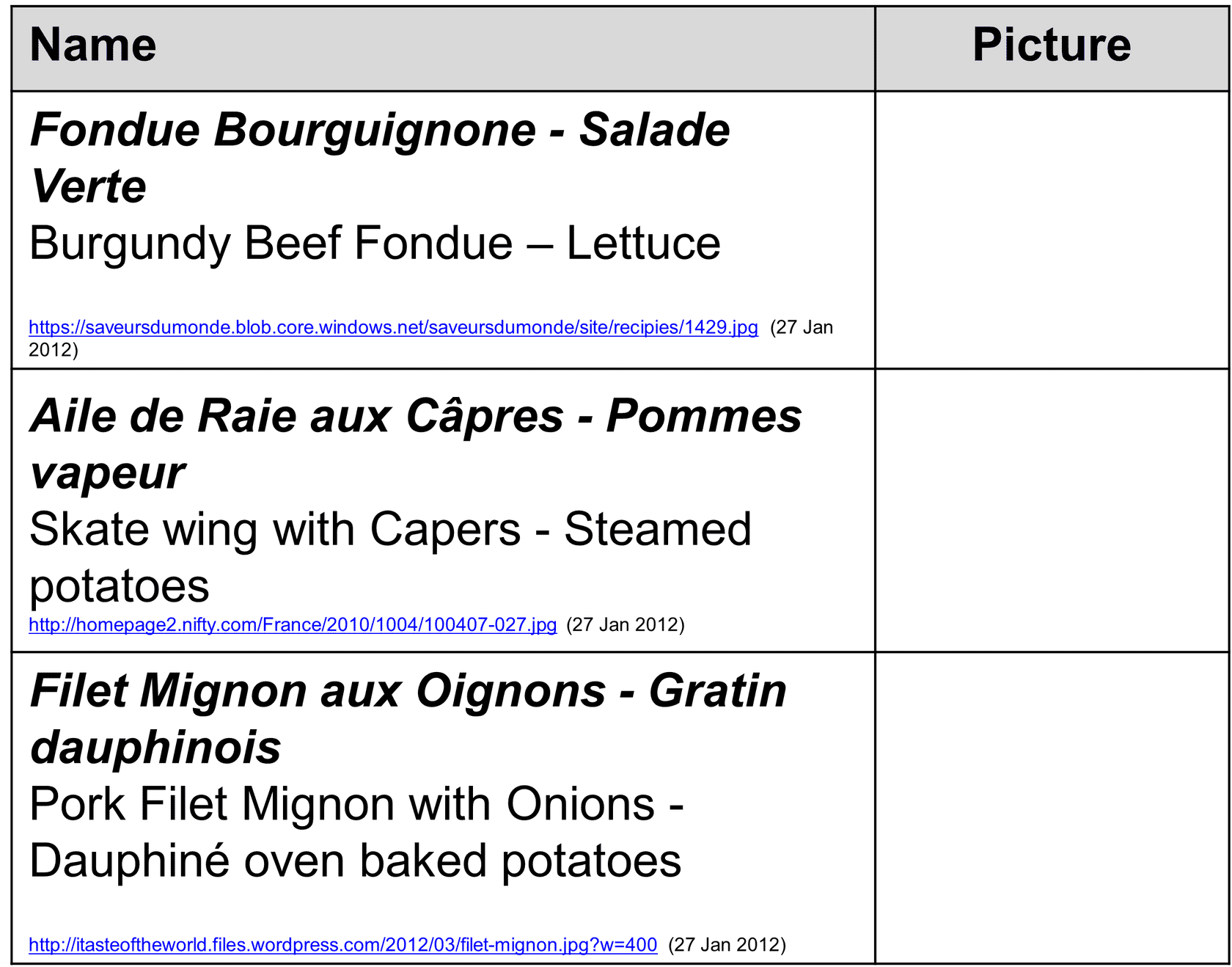
Classic Main Course and Side Dishes
Classic Cheese Board
- 1.Camembert:
- •Made of cow milk and is the national cheese of France
- •Take it our from the fridge for a few hours before serving to have a softer consistency
- 2. Brie:
- •Could be commented the same way as the Camembert
- 3.Goat milk cheese:
- •Excellent and is normally the allied of most good red wines because it brings out their flavor.
- 4. Ewe milk cheese:
- •The flavor is very authentic but sometimes too powerful for “non-initiated” people.
- •Roquefort is the most famous
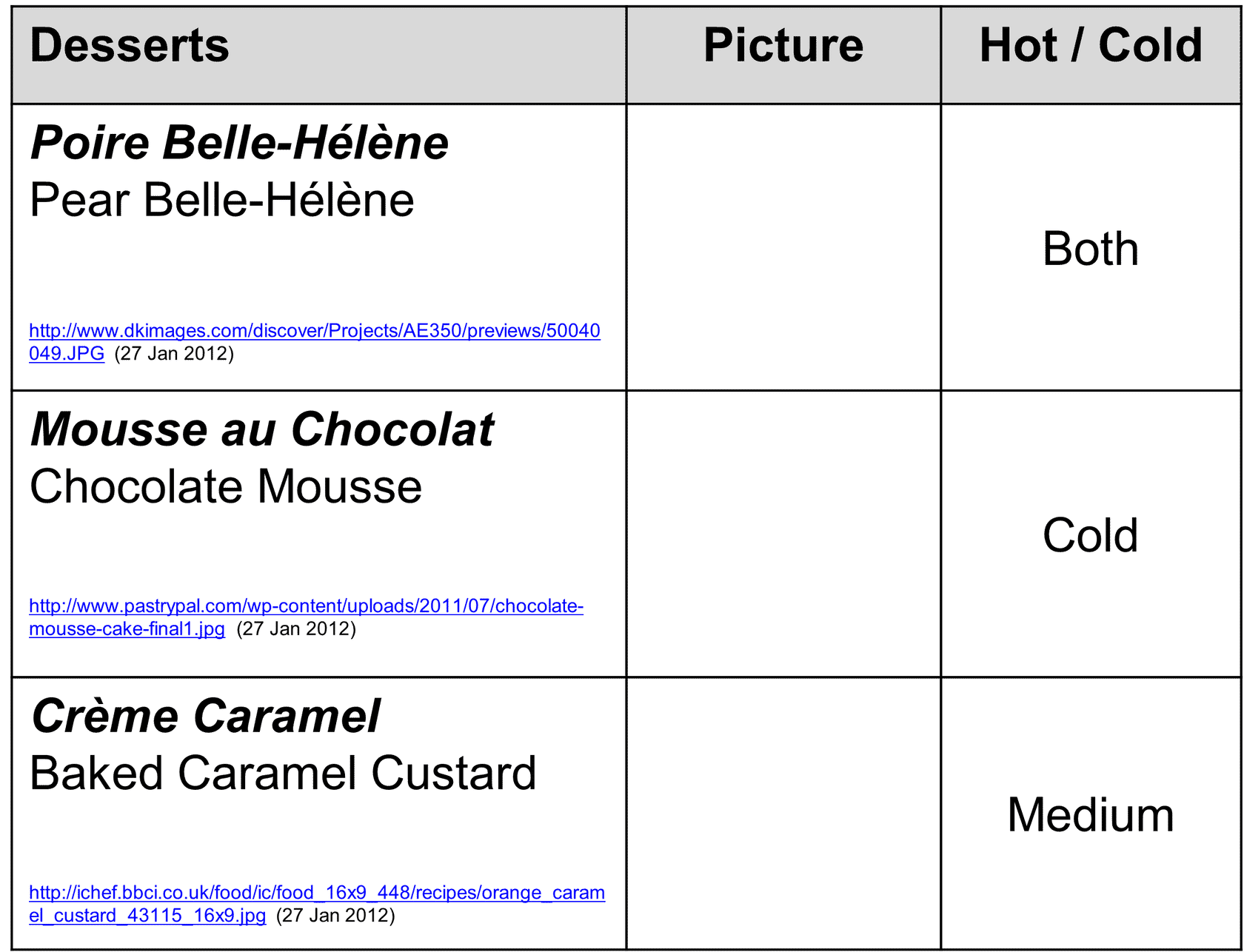
Classic Desserts
Coffee
Summary Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In purus velit, tincidunt ac nibh quis, sollicitudin varius libero. Nullam at mi felis. Donec a scelerisque augue, sit amet porttitor nibh. Suspendisse at lorem ut elit placerat blandit.
Topic 4: Singapore Cuisine
Quote: “A true Singaporean, it is said, will talk about his next meal while eating - and why not, our food is a lovely melding of at least four different cuisines-Chinese, Malay, Indian and European.”
Source from: Sylvia Tan: Singapore Heritage Food: Yesterday’s recipes for today’s cook
Recipe and videos
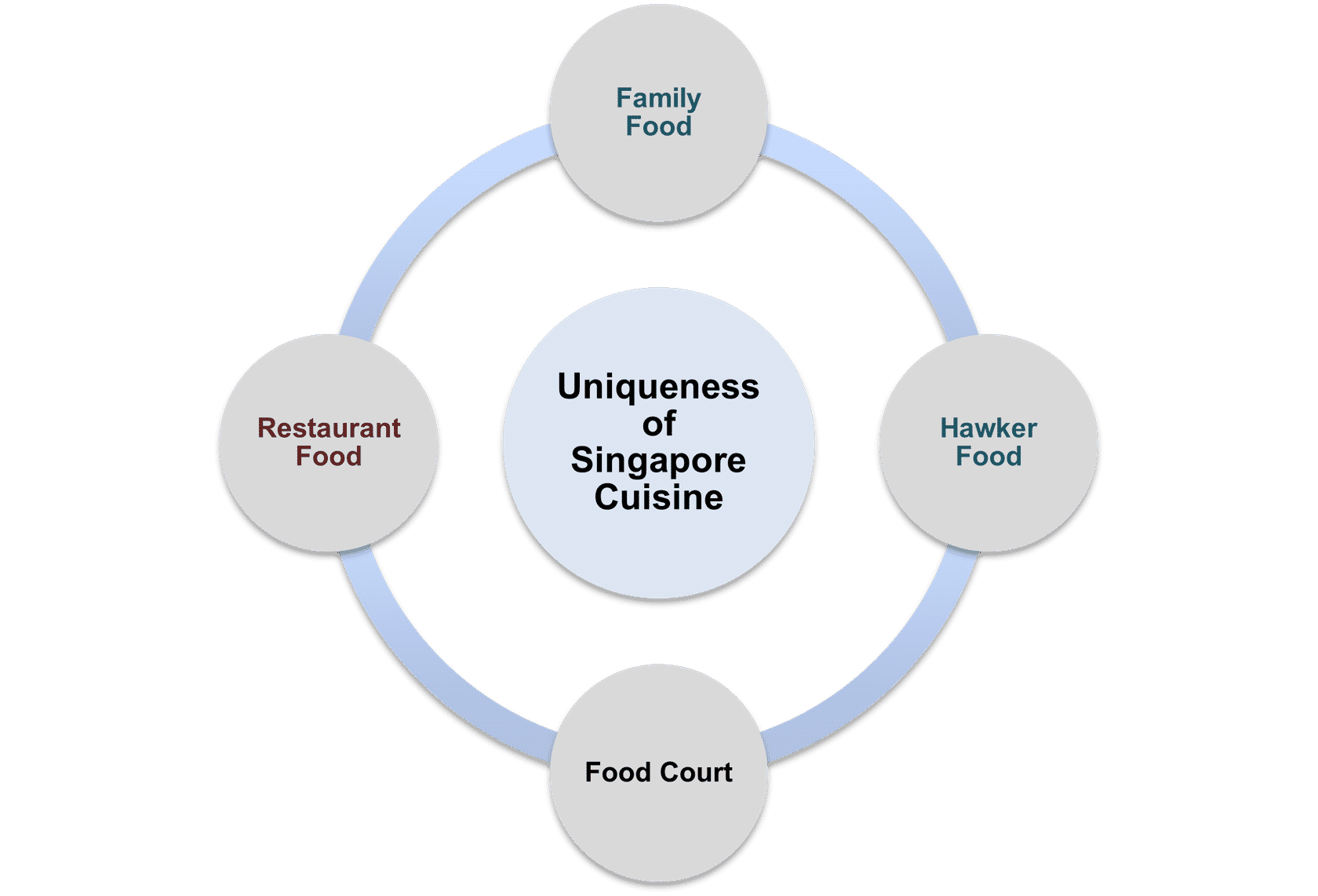
Explain the Uniqueness of Singapore Cuisine
- It is the food of the early, nameless settlement that once occupied this island.
- It is the food of Temasek, the city that grew out of the settlement under the Srivijaya empire.
- It is the food of the Sultanate.
- It is the food of traders and immigrants from:
- - Southern China
- - Southern India
- - The Arabian Peninsula
- - Indonesia
- - British colonial settlement
Popular Dishes from many cultures: some examples
- - Dim sum
- - Hainanese chicken rice
- - Hokkien mee
- - etc
Malay:
- - Satay
- - Mee rebus
- - Mee Siam
- - etc
Peranakan:
- - Kueh Pie Tee
- - Ayam Buah Keluak
- - Sayur Lodeh
- - etc
Indian:
- - Fish Head Curry
- - Prata
- - Chicken Biryani
Modern additions:Thai:
- - Pad Thai
- - Tom Yum Soup
- - Kao Niew Ma Muang
- - etc
Vietnamese:
- - Pho
- - Spring Rolls (Goi Cuon)
- - French-Vietnamese sandwich(Banh Mi)
- - etc
- •Ground spices release their flavour more quickly than whole spices.
- •Ground spices, thyme or cumin can be added while cooking the dishes which requires less cooking time else it should be added towards the end of cooking for recipes with longer cooking time.
- •Whole spices need longer time to release their flavour. Good for soups and stews.
- •Robust herbs such as sage, thyme and bay leaves stand up well in long cooking.
- •Milder herbs like basil, marjoram and parsley can be added at the last minute for best results.
- •For leafy herbs, rub them with the palms of your hands to release the flavour and aroma.
The making of Spice paste
- Mortar and pestle
- Cut all the ingredients into small pieces. This will shorten the time of pounding and will make the paste finer. Start with the dry and hard ingredients for pounding e.g. fennel seed, ginger, turmeric or lemon grass. Roast or toast dried spices before adding into the mortar. This is to release the flavour of spices. Then, add ingredients like garlic, onion and shallot. Lastly, add wet ingredients like your soaked dried chillies and fresh chillies. Pound the paste until the desired texture. (coarse, fine and very fine )
- Blender or food processor
Method:
- First, prepare ingredients.
- Then, blend the wettest ingredients (shallots and garlic).
- Next ,add drier ingredients.
- Finally, blend to the desired consistency.
Spices/Herbs: Optimize the freshness
- 1) Spices and herbs that are whole, maintain their freshness longer than those that are grounded.
- 2) Spices and herbs will keep for a long time if stored in airtight containers.
- 3) Shelf life of properly stored spices and herbs:
- - Whole spices (unground, such as peppercorns, whole allspice, caraway seeds, etc): 3-4 years
- - Ground spices (such as cumin, ginger, paprika and chilli powder: 2-4 years
- -Ground and whole leafy herbs such as basil, oregano, rosemary and most seasoning blends: 1- 3 years.
- 4) Verify freshness by the look, smell and taste:
- - Colour fading is a good indicator of flavour loss.
- - If a fresh odour or taste is not apparent, they need to be replaced.
- 5) Do not sprinkle spices and herbs directly from the bottle over a steaming pot. Steam introduced into the bottle will hasten the loss of flavour and aroma. It will also result in caking of contents.
- 6) Use a dry measuring spoon when taking out spices/herbs from the bottle/container. Moisture introduced into the bottle will also result in caking and flavour loss.
Explain the benefits of Spices and Herbs
- - As flavouring
- - As an antibiotic, expectorant and digestiive
Chives:
- - As flavouring and garnishing
- - As stimulant and digestive
Coriander:
- - As flavouring and garnishing
- - Coriander seeds: as stimulant and digestive
Lemon Grass:
- - As flavouring
- - For liver complaints
- - As anti-mosquito repellant
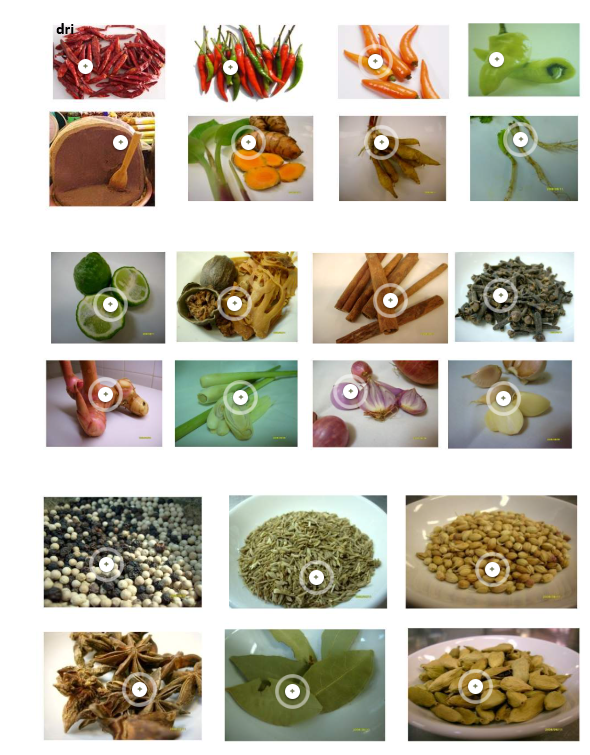
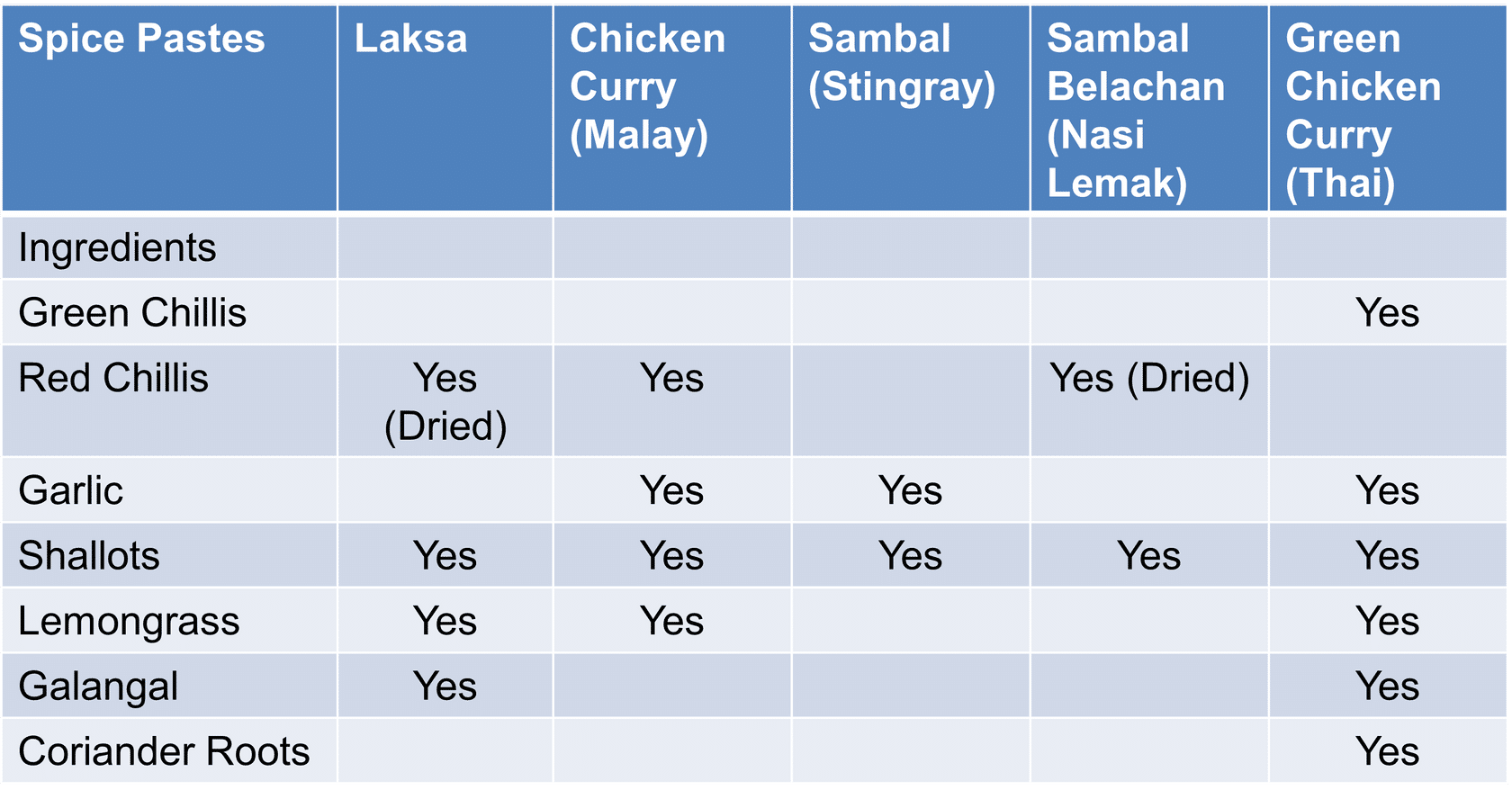
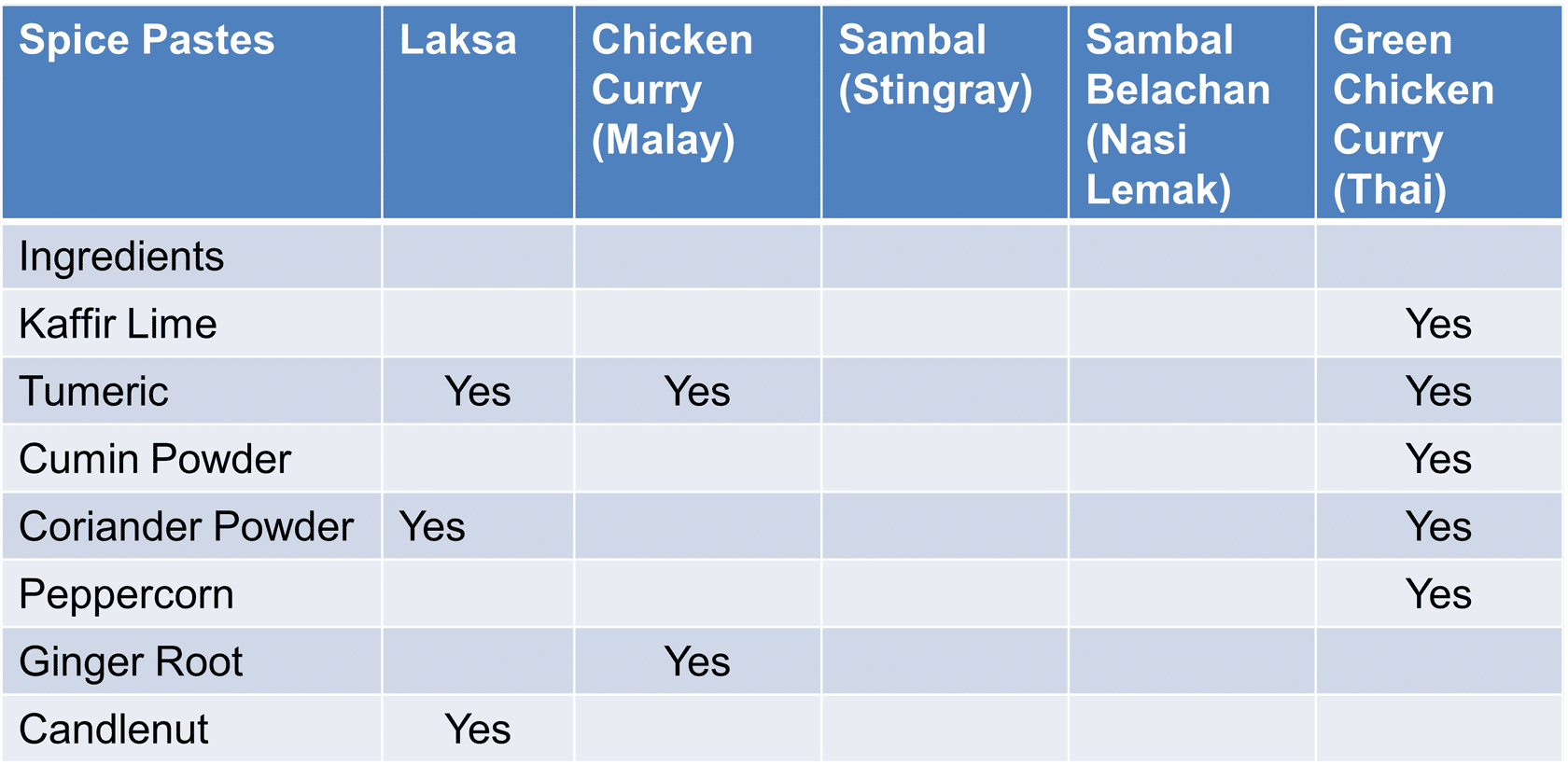
Common Spice/Herbs in Pastes: Some examples
Topic 5: Thai Cuisine
Recipe and videos
Introduction To Thai Cuisine
- Thai cuisine is collectively known as Indo-China cuisine.
- Uses common ingredients such as spices, herbs, edible plants, fruits and seafood.
- Many Thai curries are Indian-style, redolent of chillies, garlic, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon and onions.
Popular Thai Dishes
- Tom Yam Goong - Hot and sour prawn soup Gaeng Kiaw Waan Gai - Green curry chicken
- Pad Thai - Stir-fried noodles Thai style
- Som Tam Thai- Green Papaya Salad
- Pad Kra Pao- Stir-fried beef or Chicken with hot basil
- Gaeng Phet Pet Yang – Roasted duck in red curry
- Yam Nua Yang - Spicy grilled beef salad
- Moo Sa-Teh - Barbecued pork satay
- Gai Pat Met Ma-Muang - Stir-fried chicken with cashew nut
- Pha-Naeng – Thick creamy red curry
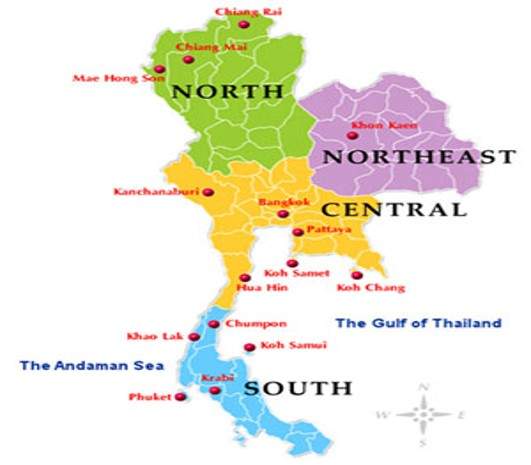
Types of Regional Dishes
Northern Thai Cuisine
- Kaeng Ho: spicy and sour dry curry made with pickled bamboo shoots and glass noodle.
- Khao Soi: curry broth with egg noodles and chicken, pork or beef; influenced from Myanmar, Laos and Chinese Muslims.
- Kaeng Hang Lay: a pork curry seasoned with ginger, tamarind and turmeric.
- Kaeng Yuak: made with banana palm hearts
- Kaeng Khanoon: made from the young jackfruit.
Central Thai Cuisine
- Kaeng Kheow Wan: Thai green curry usually added with poultry, fish or beef.
- Kaeng Ped: Thai red curry.
- Kaeng Phanaeng: a milder version than Kaeng ped with thicker texture.
- Tom Yam, the famous hot and sour soup, which originates from the Central Region.
- Tom Kha Kai: a creamy coconut milk soup made with chicken.
- Khai Yat Sai: omelette filled with ground pork, tomato and onion.
- Khao Lam: sticky rice and coconut steamed in a length of bamboo.
Northeast Thai Cuisine
- Somtam: the green papaya is tossed in a mortar with lime juice, garlic, fish sauce and a number of other ingredients. A popular style has dried shrimp, cherry tomatoes and roasted peanuts. Another has pickled field crab and very pungent fermented fish sauce called Pla Ra.
- Kai Yang or grilled chicken: the art lies in the preparation of garlic, coriander root, black pepper and fish sauce that is rubbed over the chicken before it is cooked slowly over hot charcoal. A variety of dips are served with the chicken, and sometimes with a heap of garlic shavings.
Southern Thai Cuisine
- Kaeng Tai Pla: a very hot curry made with fish stomach, green beans, pickled bamboo shoots and potato. Fresh turmeric turns this and many other southern curries a distinctive yellow.
- Kaeng Leuang or yellow curry: made from fish, green squash, pineapple, green beans and green papaya.
- Khanom Chin: is made of thin fresh rice noodles which appears as a spicy Malay style fish curry sauce, served with dishes of cucumber, pineapple, pickled cabbage and other fruits and vegetables.
- Kai Betong: (named after the town of Betong on the Thai-Malaysian border) consists of steamed chicken seasoned with soy sauce and then stir-fried with green vegetables.
Common Ingredients in Thai Cuisine
- dried red spure chili, bird's eye chilli, yellow spur chilli, bell chilli
- shrimp paste, turmeric, key ginger, coriander roots
- kaffir lime rind, Nutmeg and Mace, cinnamon, cloves
- Galangal, Lemonngrass, shallots, galic
- white and black peppercorns, cumin seeds, coriander seeds,
- star anise, bay leaves, cardamom
Quality Standards
Prepare Paste
Prepare Paste for Cooking Thai Curry Dishes (Expected Duration 15 mins )
- - Choose the correct type of mortar and pestle.
- - Understand techniques of grinding, crushing and bashing.
- - Fill the mortar only to 1/3 of its capacity.
- - For whole spices, crush them first and grind lightly with the sides of the pestle and then pound gently with the broad end of the pestle.
- - Grind all the dry ingredients first.
- - Pound till desire consistency.
Common Characteristic of Thai Cuisine Dishes
- Known for its balance of hot (spicy), sour, sweet, and salty taste .
- Naam Plaa (Thai น้ำปลา), a very aromatic and strong-tasting fish sauce, an important ingredient in Thai cooking.
- A full meal consists of many complementary dishes.
Common Characteristic of Regional Thai Cuisine Dishes
- Prik Nam Som: This is basically sliced chilli (prik) in vinegar (Nam Som). Gives a sour taste.
- Nam Plaa: Fish sauce which basically gives a salty flavour.
- Prik Pon: Dried red chili which is either flaked or ground to a powder. This gives the heat.
- Nam Taan: Which is normal white sugar. The sweetness can be blended to balance the strong flavour in Thai food.
Topic 6: Chinese Cuisine
Recipe and videos
Identify Eight Regional Cuisines
- Guangdong: light, crispy and fresh
- Zhejiang: Soft texture, sweet taste
- Fujian: Fermented ingredients, soft texture, dry and fresh seafood
- Anhui: sweet, keeps the natural flavor, uses a lot of wild ingredients.
- Hunan: spicy, salty, uses a lot of fermented ingredients
- Jiangsu: Natural flavor retained from the original stock with a mixture of salty and sweet taste
- SzeChuan: Numb spicy and oily
- Shandong: Tender, greasy salty and some sweet flavor
Identify Culinary Basics
- No Single “Chinese” Cuisine
- - Geographical reasons
- - Four climate zones
- •North : Hearty dishes
- - Temperature could fall below minus 13°
- - Meals needs to be warming and nourishing
- - Famous for good solid dishes with generous amount of garlic, onions, black bean paste and cabbage
- •South : Creative
- - Regarded by the Chinese as being imaginative and delectable
- - Dogs and cats as an acquired taste
- - Exotic ingredients : snakes, turtle, sea cucumber and shark’s fin
- •East : Mild dishes
- - Cuisine is generally fresh and mild in flavor
- - Seasoning is more subtle in Jiangsu, Anhui, Shanghai and Zhejiang
- - Chili or other hot seasoning are seldom use
- •West : The spicy and Hot
- - Szechuan and Hunan with very fiery taste and flavor
- - Main flavor comes from the chili and Szechuan pepper
- - Vinegar, sesame, oil and bamboo shoot are essential
Describe Eating Etiquette
- The meat and vegetable dishes are all laid out in the center of the table
- •Diners eat directly from the communal plates using their chopsticks and spoons
- •Soup is also consumed from the common bowl (now, separate bowls)
- •Chinese dining tables are more likely to be square in small restaurants and street foods. Round tables are in larger establishments
Topic 7: Basic Dessert
Recipe and videos
Key tools and equipment
- weighting scale, valume measures (spoon/cup/liquid measures), knife(bread knife, paring knife, chef knife)
- thermometer, cookware(saute pan, crepe pan), baking trays(sheet pan, loaf pan, cupcake tray, tube pan, silicon modules, tart pan and ring, spring form)
- modules, cake rings, mixing bowl,
- hand tool(brush/scrape/spatula/whisk/peeler/zester/scissor), for piping(bags and nozzels), ovens
- oven rack, cooling rack, mixer(planetary or hand type)
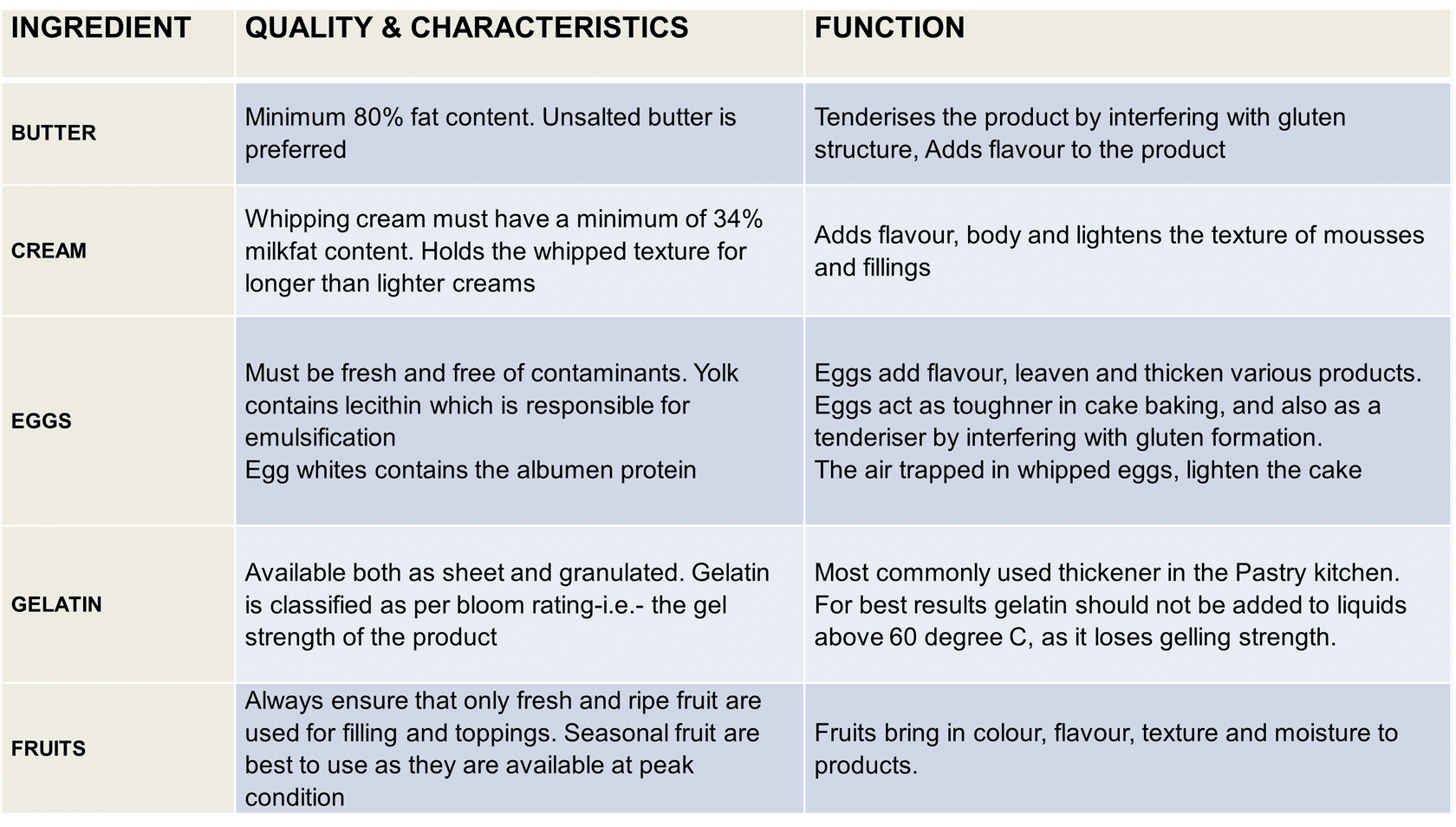
BAKING INGREDIENTS
BAKING INGREDIENTS- Types, characteristics, functions and quality indicators
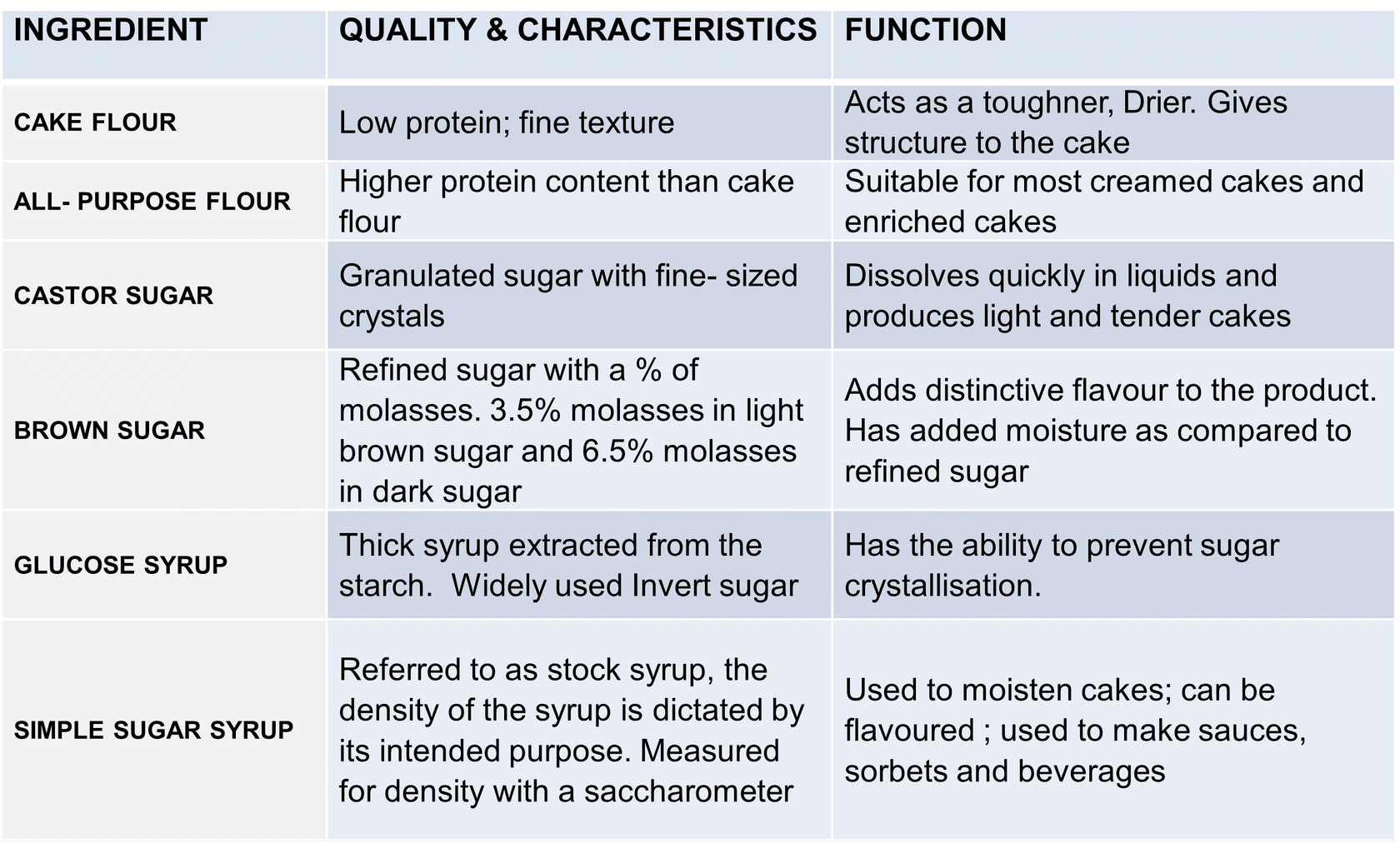
- Castor sugar (also spelled caster sugar) is a type of very fine granulated white sugar.
- Molasses is a thick, dark, sticky syrup that comes from processing sugar cane or sugar beets.
- Gelatin (often spelled gelatine in British English) is a protein made from collagen. It’s used to make liquids set into a jelly or gel.
Classification of Dessert Items
Bread:
- Quick breads- scones, cornbread, American muffins
- Lean breads- Baguette, country bread, hard-rolls
- Enriched breads- Brioche, Pannetone, stollen
- Laminated breads- Croissant, Danish
Pie & Tarts
- Cream filling tarts or pies- Pumpkin pie, Pecan pie
- Custard and soft pie filling- Blueberry and cream pie,
- Fresh fruit tart
- •Fruit filling- Apple pie, Tarte Bourdaloue
- •Flans – Swiss Apple flan, Flan Parisienne
- •Traditional/ specialties- Tarte Tatin, Linzertorte
Custard and cheese cakes
- •Baked custards- Crème caramel, crème brulee
- •Stirred custards- Crème Anglaise, crème Patisserie
- •Baked cheesecake- New York cheesecake, Japanese Chessecake
Foundation Pastes
- •Choux pastry- Eclairs, churros
- •Puff Pastry-Millefeuille, Apple turnovers
- •Short crust-Pear tart, Lemon tart, chocolate tart
Fundamentals of baking and pastry
- Creaming- Beating ingredients such as fat and sugar, till light and aerated
- Blending- Incorporating ingredients until they are evenly combined
- Folding-Gently mixing a lighter ingredient such as whipped cream into a heavier ones such as chocolate ganache, to make a light product
- Kneading- Folding and pressing dough with hands or machine to develop gluten
Key Terms
- Baking- Method of using dry, hot air to cook food in a closed environment
- Mise-en-place- Scaling ingredients, preparing the same , preparing moulds , fruit etc. before baking
- Test of Doneness-To check if the product is ready, typically by piercing the baked product with a sharp tool
- Carryover cooking- The continued cooking that occurs even after an item is removed from the oven
- Caramel- Sugar cooked to a golden brown colour
- Blanching- Literally “whitening, example boiling almonds and rubbing the skin off to remove the skin Couverture- Good quality, pure chocolate with no added fats apart from cocoa butter
- Rubbing- Solid fat is cut into dry ingredients
- Sifting- the transference of dry ingredients such as flour or ground almond to aerate, separate or remove lumps
- Whipping- beating ingredients with the single purpose of aerating. A whisk is employed for whipping or whisking. Example- whipped cream
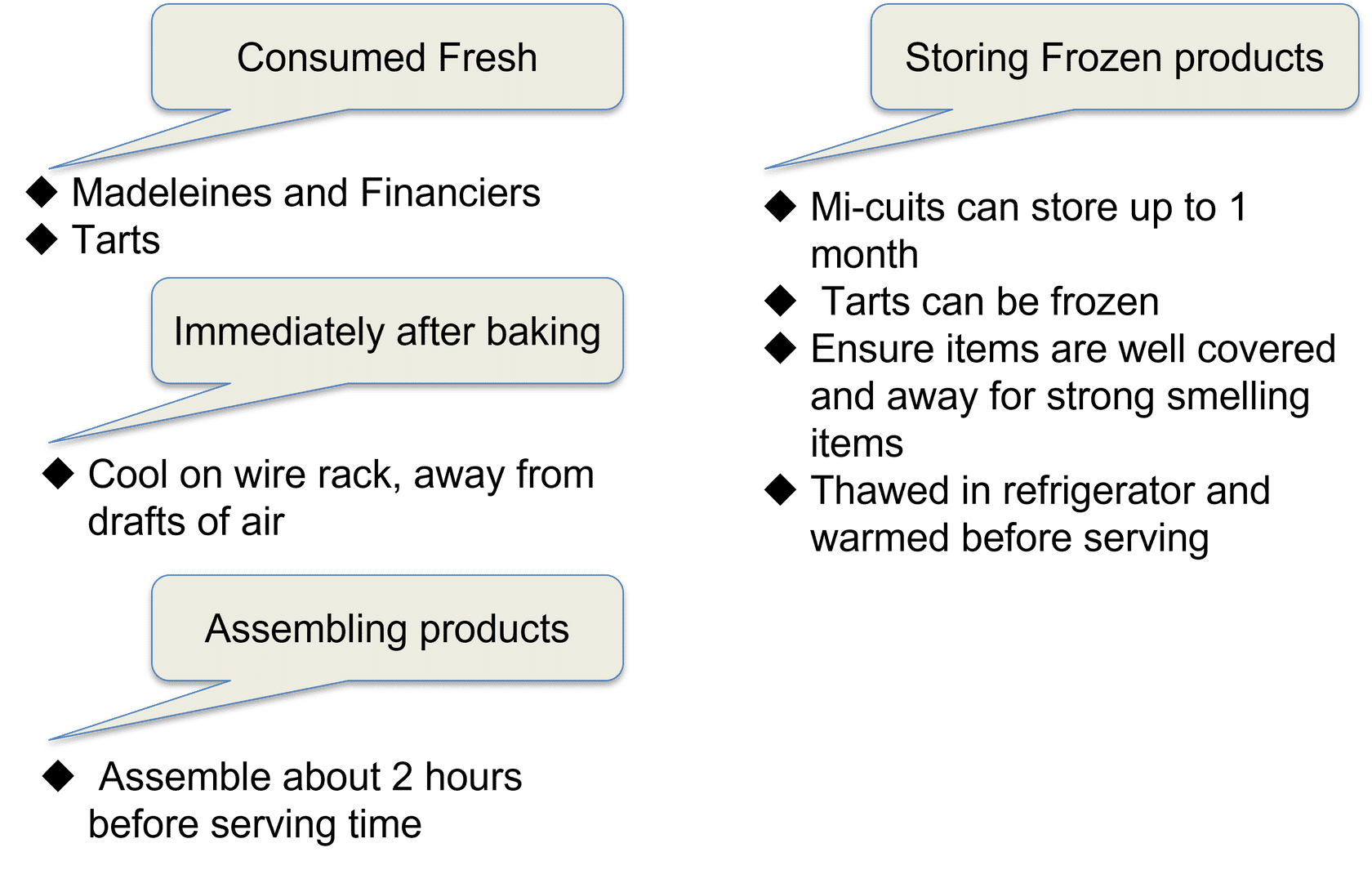
Serving and storage of pastry and bakery products
Topic 8 - Techniques of Healthy Cooking and Nutrition
Recipe and videos
Recipe backgroud
Trio-Cheese Raviolis with Pumpkin Sauce 意大利饺
- Ravioli: Italian pasta envelopes, typically small squares or circles, made from dough (flour, egg, water) filled with savory ingredients like cheese (ricotta), meat, or vegetables, and usually served with a sauce.
- cheese:
- Gorgonzola cheese
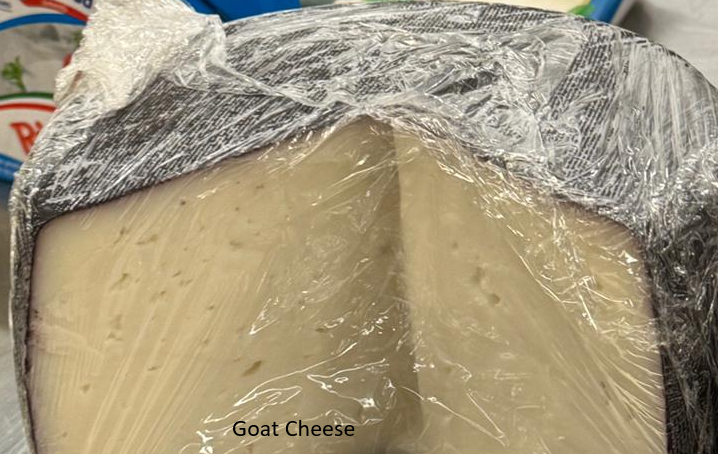
- Goat cheese
- Ricotta cheese
- nutmeg: the hard, aromatic, almost spherical seed of a tropical tree 肉豆蔻
- sage: an aromatic plant whose greyish-green leaves are used as a culinary herb, native to southern Europe and the Mediterranean. 鼠尾草
- Cooking cream vs whipping cream
- Cooking cream has lower fat (15-25%) and stabilizers, making it pourable, heat-stable for sauces/soups but won't whip,
- whipping cream (30-35% fat) whips up light and airy for toppings, with higher fat for richness in desserts, but can curdle if overheated in cooking.
minestrone 意式杂菜汤
- minestrone: a fairly thick soup containing vegetables and pasta.
- Cooked macaroni: macaroni pasta (small, tubular pasta) that has been boiled in salted water until tender yet slightly firm (al dente), ready to be served with sauces like cheese, tomato, or meat.
- macaroni pasta:small, tubular pasta 通心粉/空心粉
- pasta: 意大利面(意大利语:Pasta),一种源自意大利的主食。在意语中,广义的“pasta”一词的用法与中文的“面”相似,是泛指各种使用面粉及水制成的面类食品,但意大利面有时也会加入鸡蛋
- Oregano: an aromatic Eurasian plant related to marjoram, with small purple flowers and leaves used as a culinary herb. 牛至,又名滇香薷,欧洲语言中称为“俄勒冈”、“披萨草”或“野马郁兰”(意大利语:origano;英语:oregano、pizza herb、wild marjoram),是唇形科牛至属中的一种植物。
- tomato concasse: a French culinary term for tomatoes that have been peeled, seeded, and roughly chopped, resulting in a fresh, smooth texture without bitter skins or seeds 番茄丁
- tomato paste:a thick, intensely flavored concentrate of cooked tomatoes, made by simmering tomatoes to remove most water, then straining seeds/skins and cooking further into a rich, reddish paste used to add deep umami flavor, body, and color to sauces, soups, and stews, acting as a flavor base or thickener. 番茄糊
Insalata CapreseTomato 卡普里沙拉 (Mozzarella and Basil Salad)
- Mozzarella: 莫扎瑞拉,是源自意大利南部坎帕尼亚地区的一种淡味奶酪,以其受热后能融化并产生拉丝效果的特性而闻名,常用于披萨、千层面等菜肴,也可搭配番茄和罗勒冷吃,其传统原料是水牛奶,现代多用牛奶制成
- Roma tomatoes:also called Italian or plum tomatoes, are firm, oval-shaped tomatoes with dense, meaty flesh, few seeds, and low water content, making them ideal for sauces, pastes, canning, and roasting, though they're also great fresh because they hold shape well and don't make bread soggy
- blanch the tomatoes: briefly immerse (an item of food) in boiling water, especially as a technique for removing the skin from nuts or fruit or for preparing vegetables for further cooking
Knowledge
Essential nutrients have to be taken through food as body cannot produce them. Some provide calories or energy: Macro nutrients
Calorie:
- - The unit of energy measured by the amount of heat required to raise 1000 grams of water one degree Celsius.
- - Also written as kilocalorie or kcal.
- 1 gm of pure fat supplies 9 kcal.
1 gm of pure carbohydrate supplies 4 kcal.
1 gm of protein supplies 4 kcal.
Essential Nutrients
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Proteins
- Vitamin
- Minerals
- Water
What is Dietary Fiber ?
- • Dietary fiber is the term for several materials that make up the parts of plants your body can't digest.
- • Fiber is classified as soluble or insoluble.
- • When eaten regularly as part of a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, soluble fiber has been shown to help lower blood cholesterol.
- • Oats have the highest proportion of soluble fiber of any grain. Foods high in soluble fiber include oat bran, oatmeal, beans, peas, rice bran, barley, citrus fruits, strawberries and apple pulp
Soluble fiber vs insoluble fiber
- Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel, slowing digestion, lowering cholesterol/blood sugar (e.g., oats, beans, apples, citrus),
- insoluble fiber doesn't dissolve, adds bulk, speeds food through the gut, and prevents constipation (e.g., whole grains, nuts, wheat bran, vegetables).
- Both are crucial for health, found in most plants, but offer different digestive benefits, with soluble promoting satiety/cholesterol control and insoluble aiding regularity
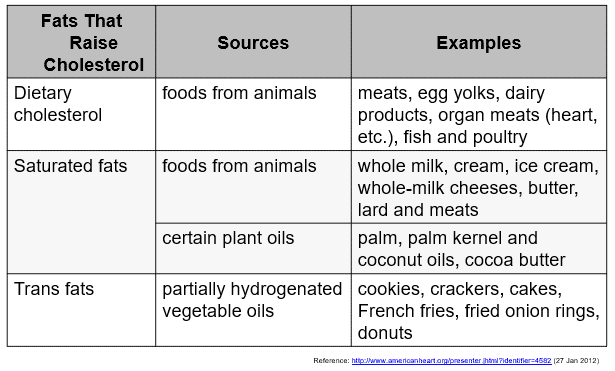
Fats that Raise Cholesterol
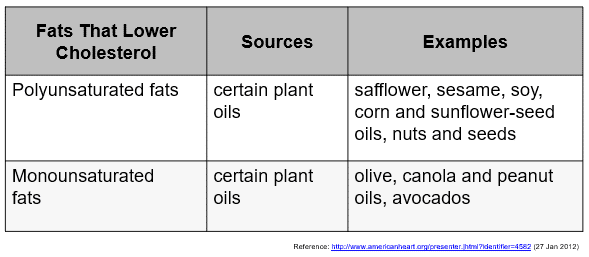
Fats that Lower Cholesterol
Importance of Proteins
- • Proteins make up about 15% of the mass of the average person.
- • Protein molecules are essential to us in an enormous variety of different ways.
- • Much of the fabric of our body is constructed from protein molecules.
- • Muscle, cartilage, ligaments, skin and hair - these are all mainly protein materials.
- • In addition to these large scale structures that hold us together, smaller protein molecules play a vital role in keeping our body working properly.
- • Hemoglobin, hormones (such as insulin), antibodies , and enzymes are all examples of these less obvious proteins.
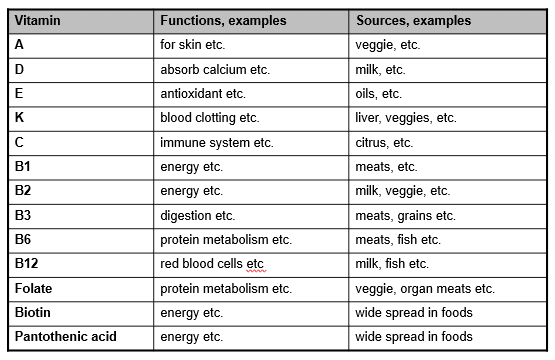
Vitamins Table
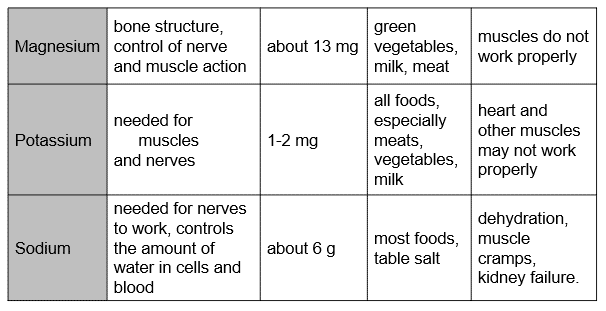
Mineral Table
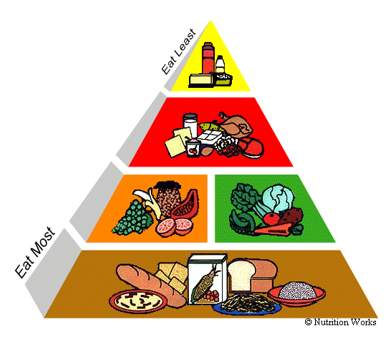
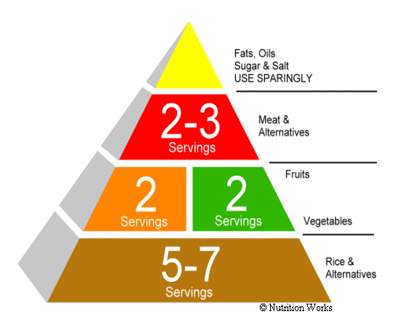
Healthy Diet Pyramid (Singapore)
- • An outline of what to eat each day. It is not a rigid prescription, but a general guide that lets you choose a healthful diet that's right for you.
- • Calls for eating a variety of foods to get the nutrients you need and at the same time the right amount of calories to maintain or improve your weight.
- • Focuses on fat because most Singaporeans diets are too high in fat, especially saturated fat.
Recommended Servings
- • The Pyramid shows a range of servings for each major food group.
- • The number of servings that are right for you depends on how many calories you need, which in turn depends on your age, sex, size, and how active you are.
- • Should have at least the lowest number of servings in the ranges.
- • The calorie based on recommendations of the Department of Nutrition and on calorie intakes reported by people.
Ingredients Substitutes and Alternatives
• Ingredient substitutes:
- – Replacement of one ingredient with another of presumably similar-although not necessarily identical-flavor, texture, appearance and other sensory characteristics.
• Ingredient alternatives:
- – Replacement of one ingredient with another different flavor, texture, appearance or other characteristic, but one that will not compromise-although it may change-the flavor of the dish.
Before Modifying Recipe
The Chef :
- – Reduce the amounts of the ingredient(s).
- – Replace the ingredient(s) with a substitute that will do the least to change the flavor or appearance of the dish.
- – Eliminate the ingredient(s).
Salt Substitutes and Alternatives
- • Salt is used liberally to enhance flavors
- • Salt substitutes are potassium chloride but not so palatable
- • Better to use less salt
- • Use lower-sodium salt
- • Use lower-sodium soy products
Artificial Sweeteners
- • Substitutes:
- – Saccharin = oldest artificial sweetener
- – Aspartame used from 1981
- – Sunnette approved in 1988
- •Alternative:
- – Sucralose
Fat Substitutes and Alternatives • Substitutes:
- – Olestra
- – Simplesse
- – Caprenin
- – Slatrim
- – Oatrim
Strategies to Preserve Nutritional Value
- • Store food properly: cold food in cold and seal in air-tight containers.
- • Keep in the crisper section of refrigerator.
- • Try washing / scrubbing than peeling.
- • Use outer leaves of cabbage etc. unless wilted.
- • Microwave, steam, roast or grill.
- • Use boiling liquid.
- • Use fresh ingredients, whole wheat flours etc.
- • Cook food quickly.