Table of Contents
Cooking
正宗韩国泡菜做法: https://home.meishichina.com/recipe-47135.html
Basic stocks
- stock: a flavorful liquid base 高湯/湯底
- roux: a cooked mixture used as a thickening agent, 面糊
- purée: /ˈpjʊəreɪ,ˈpjɔːreɪ/ a thick mixture or soup naturally thickened by blended solid ingredients. 泥,如土豆泥
- mirepoix: /ˌmɪəˈpwɑː/ 植物性调味香料
stock ingredients:
- Meat bones
- vegetable mixture (mirepoix)
- mirepoix: /ˌmɪəˈpwɑː/ a mixture of sautéed chopped vegetables used in various sauces.
- Seasoning water
Mirepoix is a mixture of: Onion, carrot and celery
- white stock
- white beef stock: 6-8 hours
- Game stock(venison): 3 hours
- brown stock
- brown beef stock (mirepoix): 6-8 hours
- brown veal stock: 6-8 hours
- fish stock and fumet: 20 minutes
- chicken stock 3-4 hours
- vegetable nage: 20 minutes plus marinating time
- vegetable sotck: 1 hour
- court-bouillon
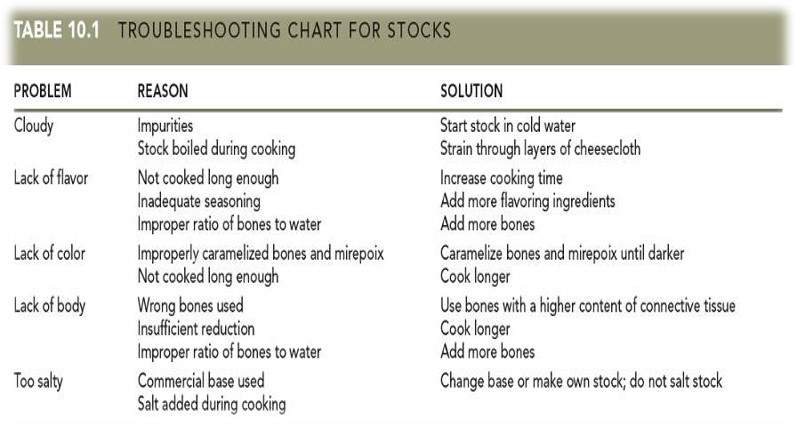
Steps in preparing the stock
- 1) Start the stock in cold water.
- 2) Simmer the stock gently.Skim the stock frequently.
- 3) Strain the stock carefully.
- 4) Cool the stock quickly (food safety: to prevent food-borne illnesses or souring.
- 5) Beware of the temperature danger zone: 5-57 degree C
- 6) Store the stock properly.
- 7) Degrease the stock.
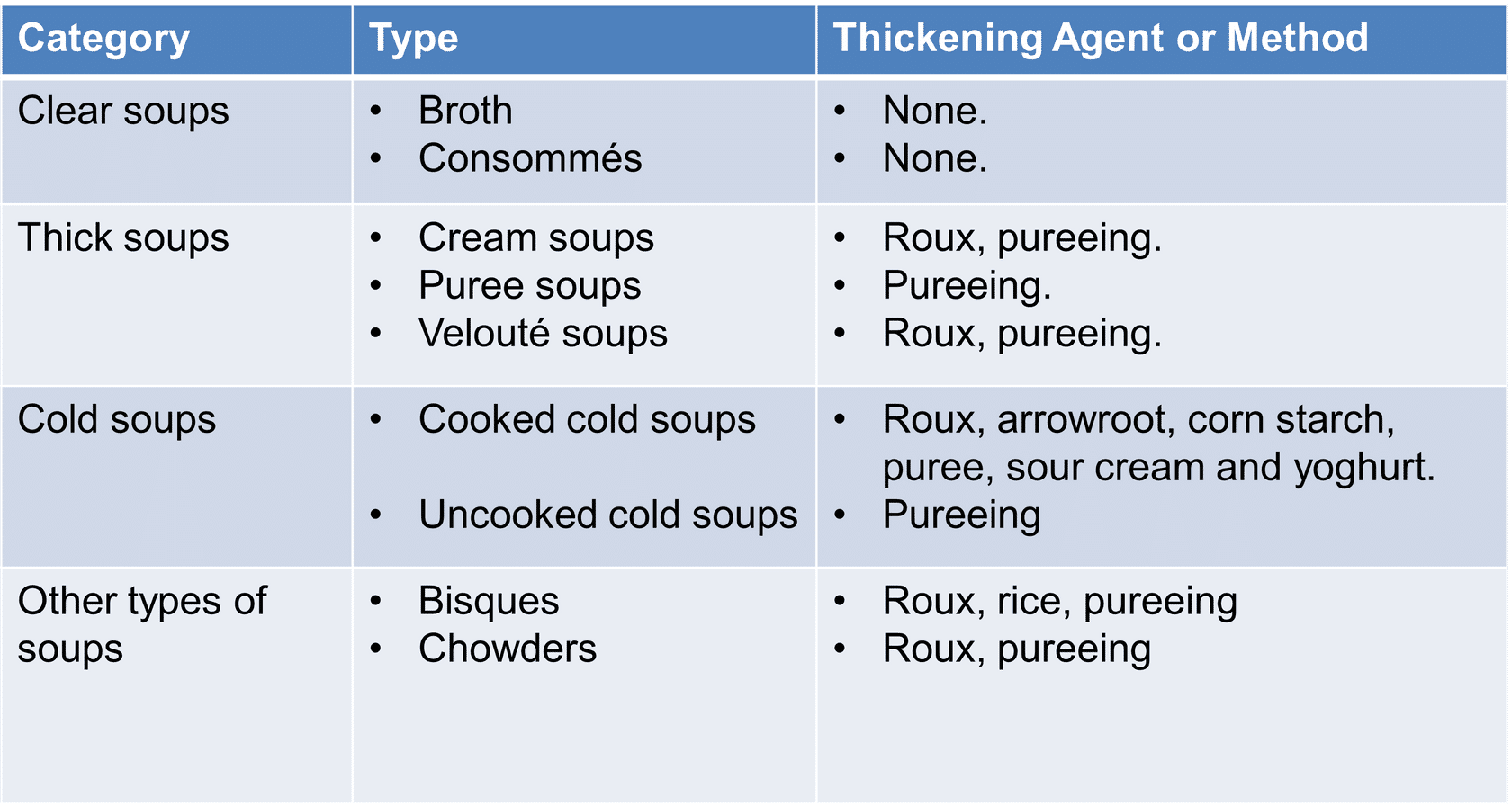
The Differences in Soups:
Clear Soups:
All clear soups start as stock or broth.
- - Broths may be served as finished items, used as the base of other soups or refined into consommés.
- Broths
- - Made from meat, poultry, fish or vegetables cooked in a liquid.
- - Full flavored broth results when a stock and not just water is used as a liquid.
- Consommés
- - Is a stock or broth that has been clarified to remove impurities.
- - Is rich and full of flavor.
Thick soups:
- Includes cream soups, velouté soups and purée soups
- Cream soups:
- Are prepared by simmering ingredients in a white stock or in thin veloutée sauce
- Mixture is strained. To finish, cream is added.
- Texture is very smooth and rich
- Example: Cream of broccoli
- Pureed soups:
- Are prepared in stock or water
- Ingredients are pureed
- Texture is slight coarse and grainy
- Example: Split pea soup
Uncooked cold soups
- Cold soups can be as simple as a chilled version of cream soup or as creatives as a cold fruit soup blended with yoghurt.
cooked cold soups
- Many cold soups are simply a chilled version of a hot soup for example consommé madrilène and consommé Portuguese.
Garnishes for Soups: Garnishes are used to add texture, flavour & visual appearance of the dish
Common garnishes for soups are:
Clear soups:
- - Fresh herbs
- - Diced or thinly shredded vegetables
- - Meat balls
Cream soups:
- - Croutons
- - Cream
- - Fresh herbs
- - Crushed dried spice and herbs
Purée soups:
- - Cream
- - Extra virgin olive oil
- - Grated cheese
Cold Soups:
- - Sour cream
- - Whipped yoghurt
- - Fruit sauce
- - Sliced fruits or cooked vegetables
Roux - Types of Roux
- White roux: Use for white sauces, e.g., béchamel where little or no colour is desired
- Blond roux: Use in ivory-Colored sauces, e.g., veloute or where a richer flavor is desired
- Brown roux: Use in brown sauces and dishes where a dark colour is desired
Preparing Roux
- Whether it will be white, blond or brown, the procedure for making the roux is the same.
- Use heavy bottom pan to prepare the roux. Heat clarified butter and add the flour and stir to form a paste.
- Cook the sauce on slow or medium heat until the desired colour is achieved.
- Brown roux requires much longer duration to develop its characteristics colour and aroma.
Method of Using Roux for Soups and Sauces
- Method A: When thickening stock with roux, either add cold stock to hot roux, or
- Method B: add cold roux to hot stock.
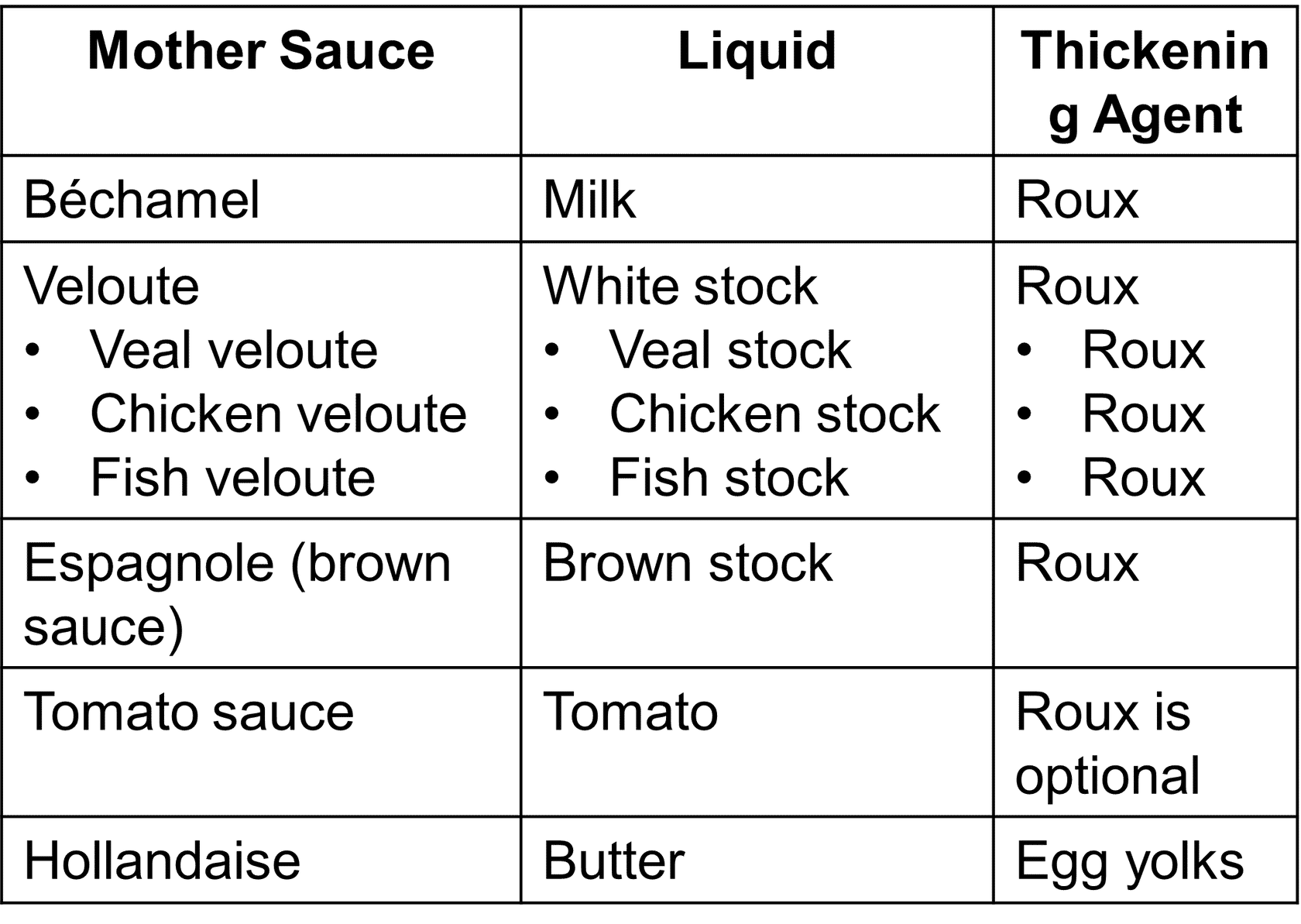
The Structure of Sauces - The Liquids, Thickening Agents, and Flavoring ingredients
- A liquid:
- - Milk (for béchamel)
- - White stock (for veloute sauces)
- - Brown stock (for brown sauce or espagnole)
- - Tomato plus stock (for tomato sauce)
- - Clarified butter (for hollandaise)
Thickening Agents:
- - Flour
- - Cornstarch
- - Arrowroot
Flavoring ingredients:
- - Lemon juice
- - Sherry
- - Cayenne
- - White pepper
Sauce Families
- Mother or Leading sauces:
- - Distinguished by the liquids and thickening agents
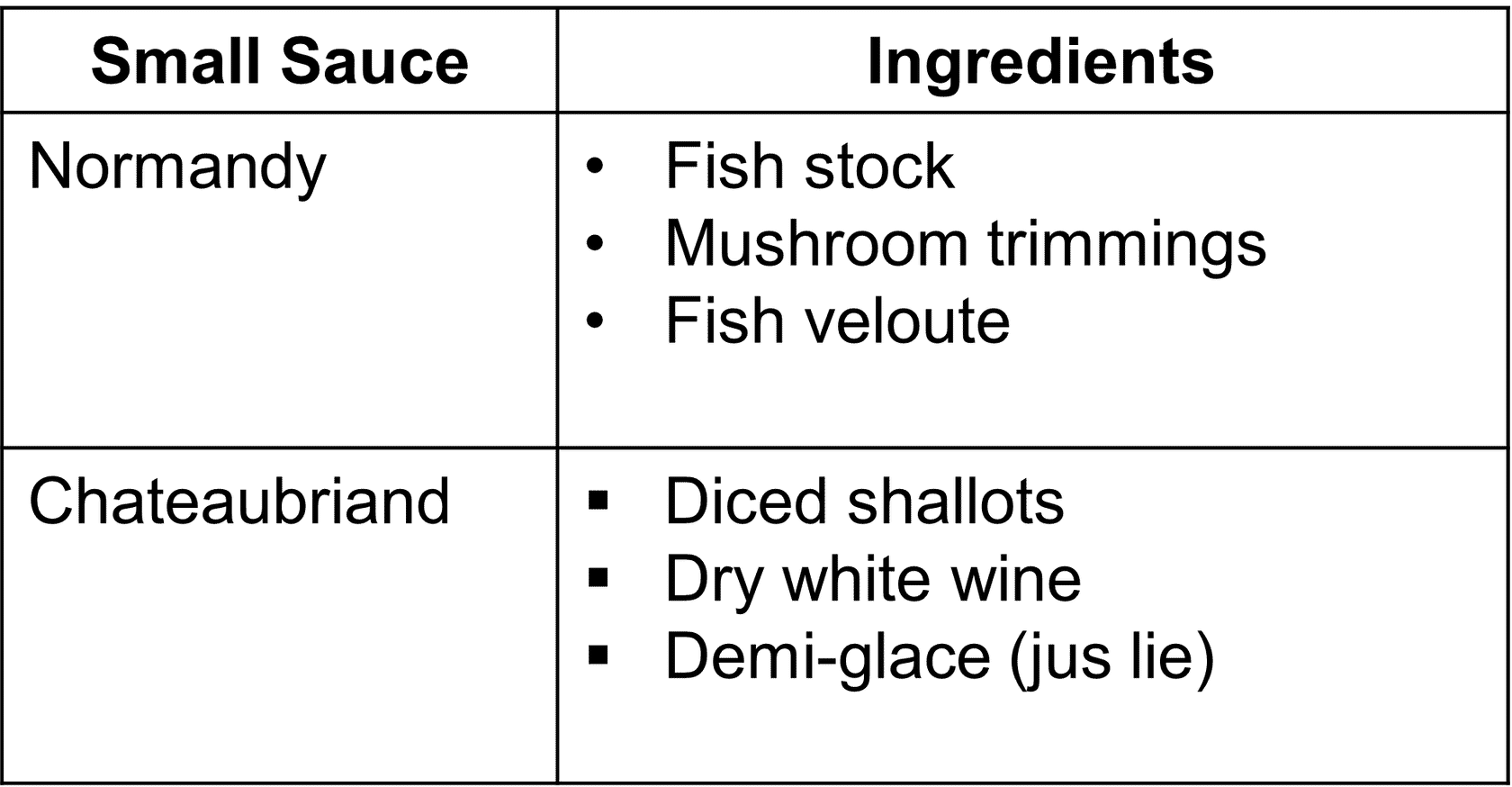
- Small or Compound sauces:
- - Are grouped into families based on their leading sauces
- - A small sauce may be named for its ingredients, place of origin or creator
Safety Alert: Handling emulsified butter sauce
Examples: Hollandaise, Bearnaise, etc
To minimize the risk of food-borne illnesses:
- - Always use clean, sanitized utensils
- - Schedule sauce production as close to the time of service as possible.
- - Never hold hollandaise sauce more than one and half hours.
- - Never mix the old batch with new one.
Essential Nutrients
Calorie:
- - The unit of energy measured by the amount of heat required to raise 1000 grams of water one degree Celsius.
- - Also written as kilocalorie or kcal.
- 1 gm of pure fat supplies 9 kcal.
- 1 gm of pure carbohydrate supplies 4 kcal.
- 1 gm of protein supplies 4 kcal.
Essential Nutrients
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Proteins
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
What is Dietary Fiber ?
- • Dietary fiber is the term for several materials that make up the parts of plants your body can't digest.
- • Fiber is classified as soluble or insoluble.
- • When eaten regularly as part of a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, soluble fiber has been shown to help lower blood cholesterol.
- • Oats have the highest proportion of soluble fiber of any grain. Foods high in soluble fiber include oat bran, oatmeal, beans, peas, rice bran, barley, citrus fruits, strawberries and apple pulp
Note: Vegetables are arguably the healthiest of all the food groups and are a great source of fiber.
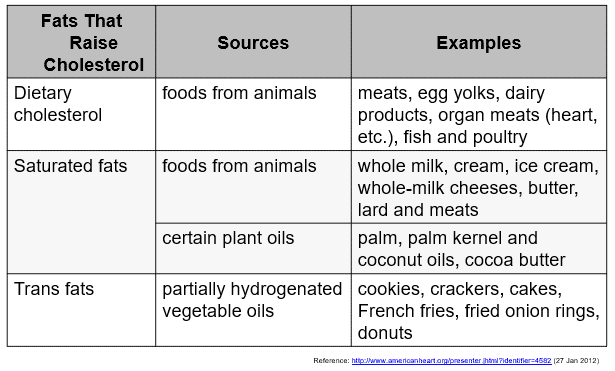
Fats that Raise Cholesterol
- dietary cholesterol: 膳食胆固醇 / 饮食胆固醇
- saturated fat: 饱和脂肪(饱和脂肪酸)
- Trans fat: 反式脂肪(反式脂肪酸)是一种对健康最不利的脂肪
- Partially hydrogenated oil(部分氢化油)
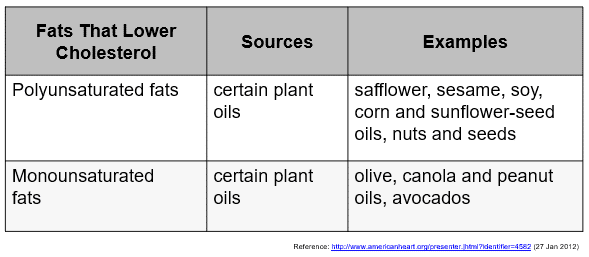
- Polyunsaturated fats:多不饱和脂肪(多不饱和脂肪酸)
- 常见的多不饱和脂肪类型:
- Omega-3 脂肪酸(很重要 ✅)
- 三文鱼、沙丁鱼、鲭鱼
- 亚麻籽、奇亚籽、核桃
- 作用:护心、抗炎、降甘油三酯
- Omega-6 脂肪酸
- 大豆油、玉米油、葵花籽油
- 坚果、种子
- 作用:必需脂肪酸,但不宜过量
Importance of Proteins
- Proteins make up about 15% of the mass of the average person.
- Protein molecules are essential to us in an enormous variety of different ways.
- Much of the fabric of our body is constructed from protein molecules.
- Muscle, cartilage, ligaments, skin and hair - these are all mainly protein materials.
- In addition to these large scale structures that hold us together, smaller protein molecules play a vital role in keeping our body working properly.
- Hemoglobin, hormones (such as insulin), antibodies , and enzymes are all examples of these less obvious proteins.
Note: Chicken breast is one of the most popular cuts of chicken. A skinless, cooked chicken breast (172 grams) contains 54 grams of protein.
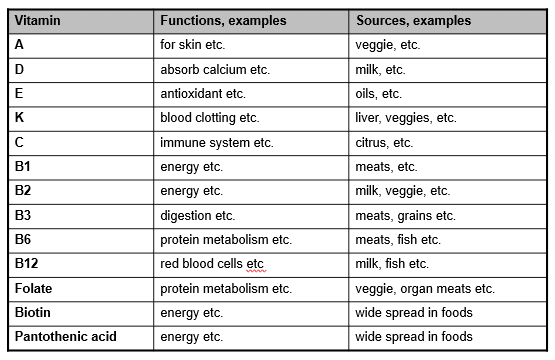
Vitamins Table
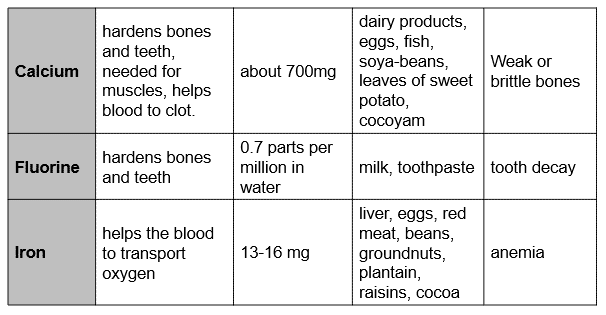
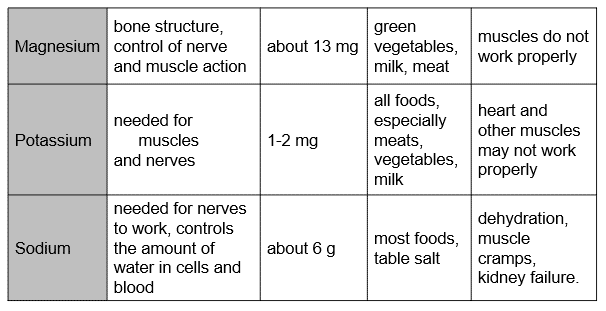
Mineral Table
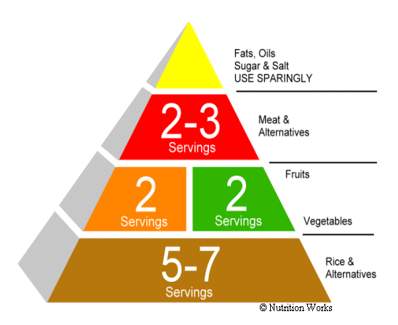
Healthy Diet Pyramid (Singapore)
- • The Pyramid shows a range of servings for each major food group.
- • The number of servings that are right for you depends on how many calories you need, which in turn depends on your age, sex, size, and how active you are.
- • Should have at least the lowest number of servings in the ranges.
- • The calorie based on recommendations of the Department of Nutrition and on calorie intakes reported by people.
Ingredients Substitutes and Alternatives
• Ingredient substitutes:
– Replacement of one ingredient with another of presumably similar-although not necessarily identical-flavor, texture, appearance and other sensory characteristics.
• Ingredient alternatives:
– Replacement of one ingredient with another different flavor, texture, appearance or other characteristic, but one that will not compromise-although it may change-the flavor of the dish.
Before Modifying Recipe
The Chef :
- – Reduce the amounts of the ingredient(s).
- – Replace the ingredient(s) with a substitute that will do the least to change the flavor or appearance of the dish.
- – Eliminate the ingredient(s).
Salt Substitutes and Alternatives
- • Salt is used liberally to enhance flavors
- • Salt substitutes are potassium chloride but not so palatable
- • Better to use less salt
- • Use lower-sodium salt
- • Use lower-sodium soy products
Artificial Sweeteners
- • Substitutes:
- – Saccharin = oldest artificial sweetener
- – Aspartame used from 1981
- – Sunnette approved in 1988
- •Alternative:
- – Sucralose
Fat Substitutes and Alternatives
• Substitutes:
- – Olestra
- – Simplesse
- – Caprenin
- – Slatrim
- – Oatrim
Strategies to Preserve Nutritional Value
- • Store food properly: cold food in cold and seal in air-tight containers.
- • Keep in the crisper section of refrigerator.
- • Try washing / scrubbing than peeling.
- • Use outer leaves of cabbage etc. unless wilted.
- • Microwave, steam, roast or grill.
- • Use boiling liquid.
- • Use fresh ingredients, whole wheat flours etc.
- • Cook food quickly.