mywiki:ejtag
Jtag/Ejtag
| Reference | jtag_training.pdf |
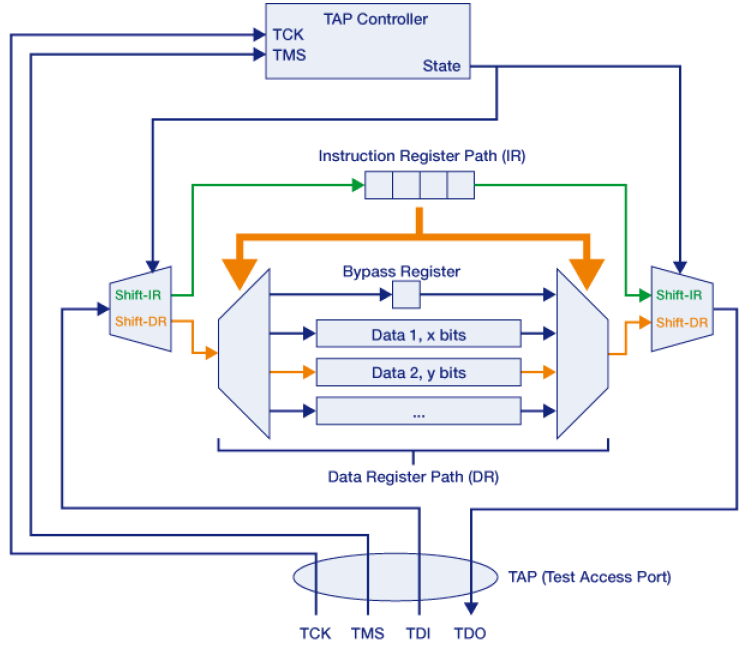
The JTAG interface, collectively known as a Test Access Port(TAP), uses the following signals to support the operation of boundary scan.
| TCK | Test Clock | this signal synchronizes the internal state machine operations. |
| TMS | Test Mode Select | controls the TAP controller state transitions |
| TDI | Test Data In | serial data from debugger to target |
| TDO | Test Data Out | serial data from target to debugger |
| TRST | Test Reset | optional, resets the TAP controller |
The functionality usually offered by JTAG is Debug Access and Boundary Scan:
- Sebug Access is used by debugger tools to access the internals of a chip making its resources and functionality available and modifiable, e.g. registers, memories and the system state.
- Boundary Scan is used by hardware test tools to test the physical connection of a device, e.g. on a PCB. Although this is usually not the task of a debugger tool the TRACE32 debugger offers mechanisms to access the JTAG TAP in a generic way, e.g. to perform boundary scan using a PRACTICE script or a custom application.
Registers
| IR | Instruction Register |
| DR | Data Registers |
The width of the IR is not specified by the JTAG standard but needs to be the same for all instructions of a specific device. Since the DR is selected according to the loaded instruction the DR width is variable.
mywiki/ejtag.txt · Last modified: by 127.0.0.1