Table of Contents
GPON
| Reference | pon.ppt | GPON Fundamental | GPON PPT(Chinese) |
Architecture
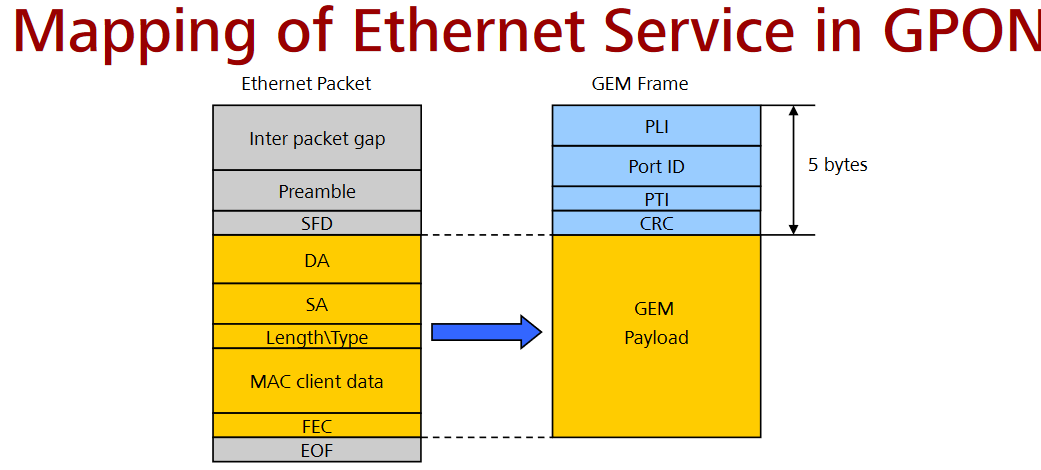
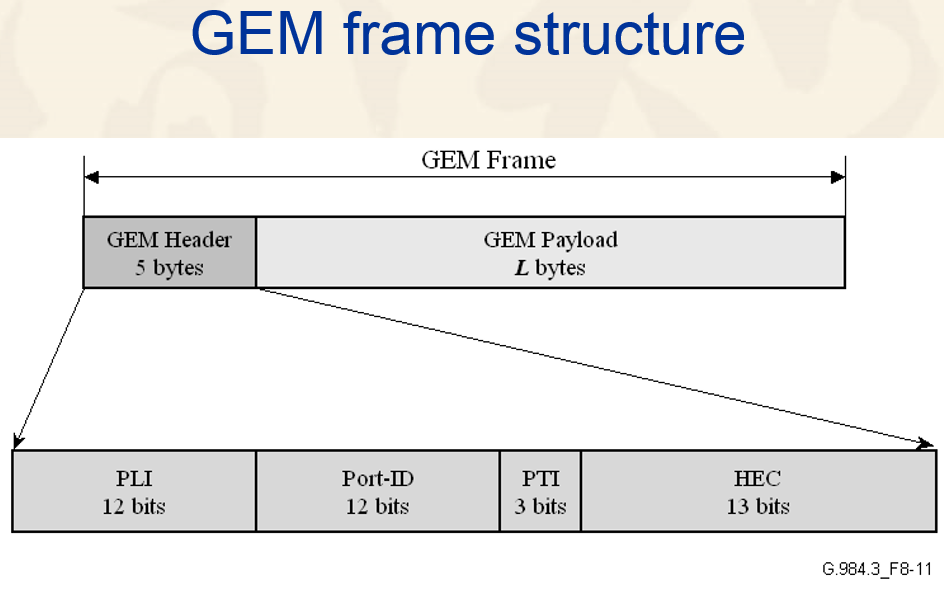
GEM Format
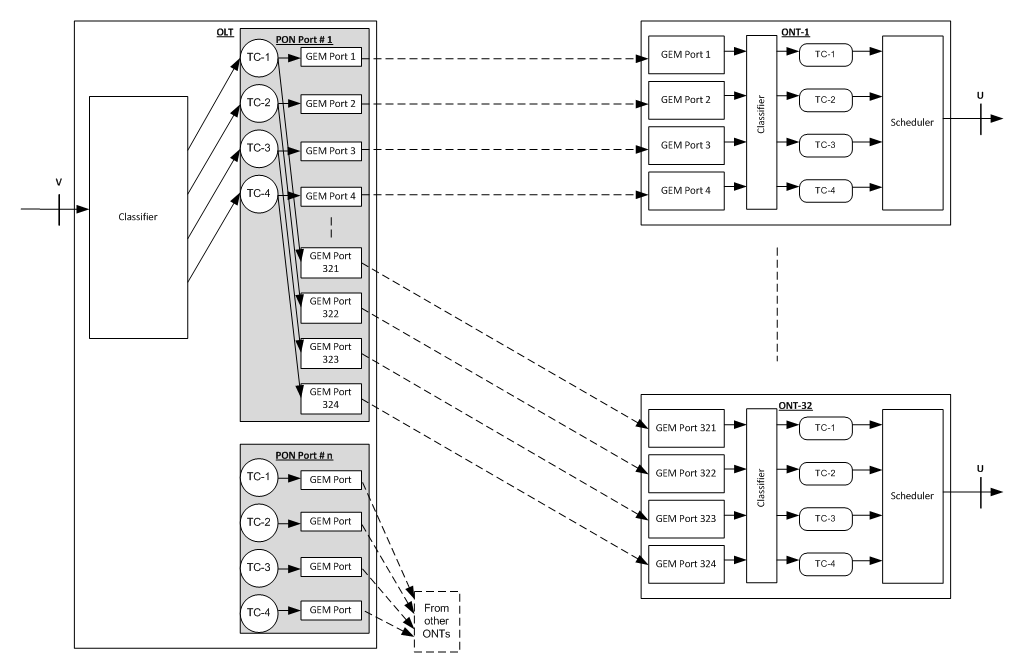
There are 2 types of GEM Channels:
Downstream-only GEM Channels - These channels are used to transmit downstream broadcast/multicast traffic from OLT to all ONTs. The ONTs identify traffic meant for them based on GEM Port ID. Bi-directional GEM Channels - These channels are used for upstream and downstream traffic between the OLT and the ONT. The frames are transmitted from the OLT into the GPON interface and are forwarded only on the U interface of the ONT on which that GEM Port has been assigned.
Transmission convergence layer

Types of PONs
| APON | ATM PON |
| BPON | Broadband PON |
| GPON | Gigabit PON |
| EPON | Ethernet PON |
| GEPON | Gigabit Ethernet PON |
| CPON | CDMA PON |
| WPON | WDM PON |
GEM Related Definitions
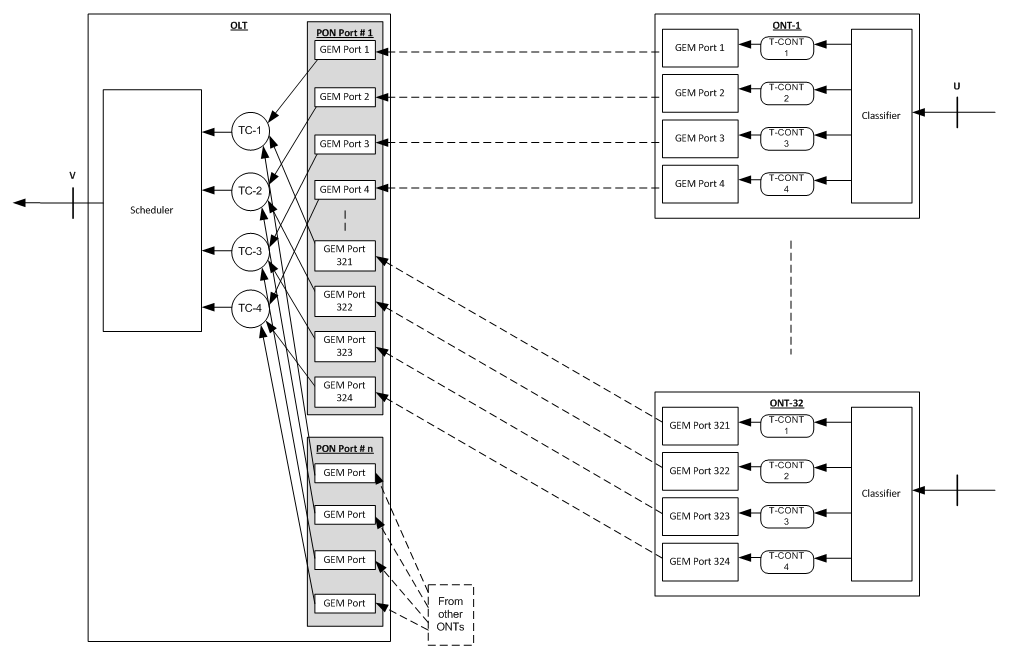
T-CONT:
A traffic bearing object within an ONT that represents a group of logical connections, and is treated as a single entity for the purpose of upstream bandwidth assignment on the PON. In the upstream direction, it is used to bear the service traffic. Each T-CONT corresponds to service traffic of one bandwidth type. Each bandwidth type has its own QoS feature.
ALLOC_ID:
Each T-CONT is identified by the ALLOC_ID uniquely. The ALLOC_ID ranges from 0 to 4095. It is allocated by OLT i.e. a T-CONT, and can only be used by one ONT per PON interface on the OLT.
GEM Port:
A GPON Encapsulation Method (GEM) port is a virtual port for performing GEM encapsulation for transmitting frames between the OLT and the ONT. Each different traffic-class (TC) per UNI is assigned a different GEM Port. Each T-CONT consists of one or more GEM Ports. Each GEM port bears one kind of service traffic i.e. a T-CONT type.
GEM Port ID:
Each GEM Port is identified by a port ID uniquely. The Port ID ranges from 0 to 4095. It is allocated by the OLT, i.e. a GEM port, and can only be used by a single ONT per PON interface on the OLT.
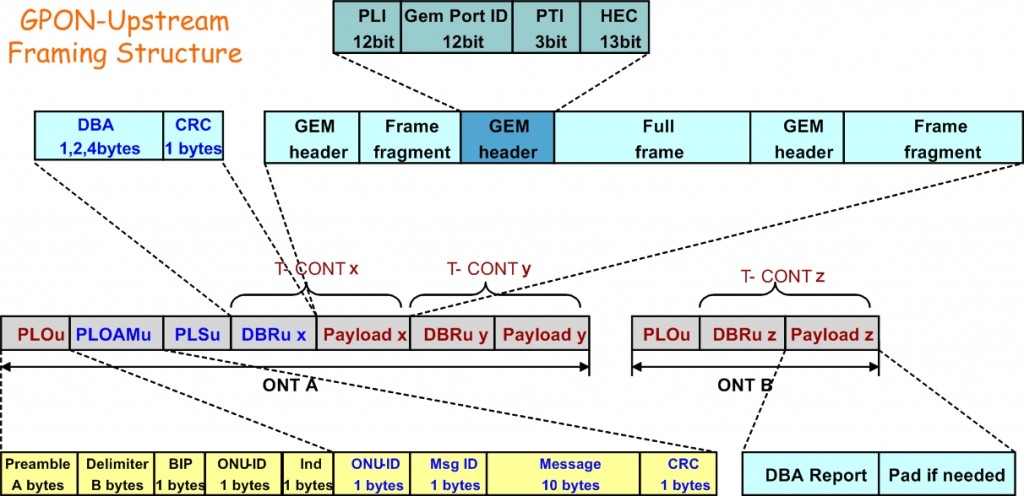
US(UpStream) GPON format
PLOu: Physical Layer Overhead upstream
always sent by ONU when taking over from another ONU contains preamble and delimiter (lengths set by OLT in PLOAMd) BIP (1B), ONU-ID (1B), and Indication of real-time status (1B)
PLOAMu: PLOAM upstream (13B) – messaging with PLOAMd
PLSu: Power Levelling Sequence upstream (120B)
used during power-set and power-change to help set ONU power so that OLT sees similar power from all ONUs
DBRu: Dynamic Bandwidth Report upstream
sends traffic status to OLT in order to enable DBA computation
Payload: Payload data, may be a data frame or DBA status report,Payload=(DBA Report+Pad)/(Gem Header+Gem Frame)
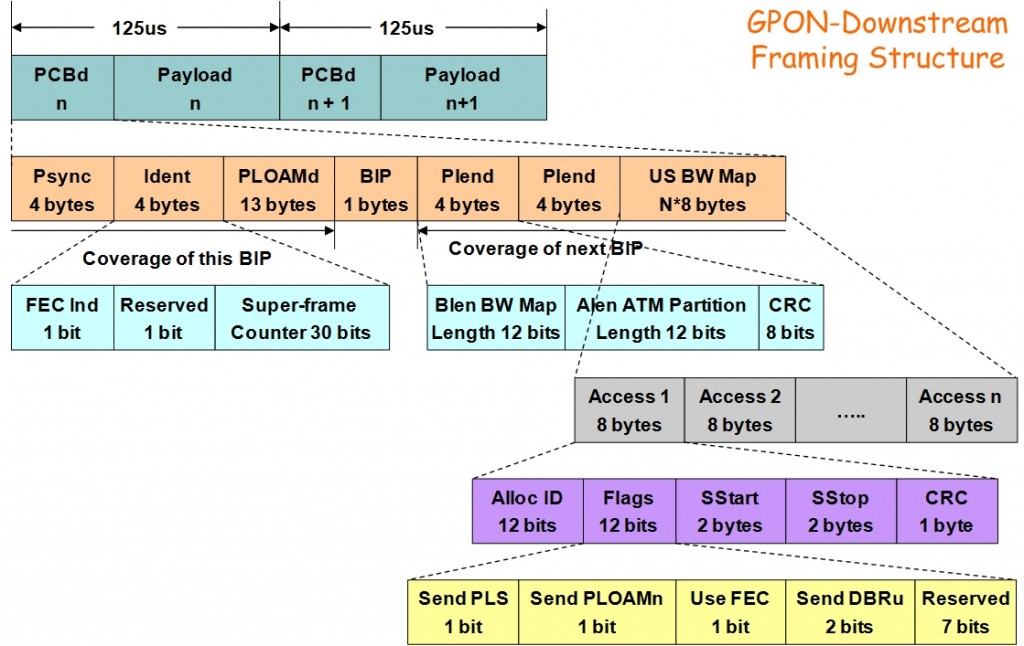
Downstream Frame structure
Each GTC (GPON Transmission Convergence) frame consists of PCBd (Physical Control Block downstream) and payload.
PCBd contains sync, OAM, DBA info, etc. payload may have ATM and GEM partitions (either one or both);
Downlink frame’s fixed 125us frequency is 8000Hz,and it’s size is 38,880 bytes, when speed rate reaching 2.488Gbps.
GTC payload potentially has 2 sections:
ATM partition (Alen * 53 bytes in length). GEM partition (now preferred method);
Because GTC payload definitely is the “payload” of GEM Frame in downstream. So firstly let’s focus our attention on PCBd,the downlink control information frame’s header.
Psync:
Synchronization for olt and onu.(4 bytes)
Ident:
MSB indicates if FEC is used, 30 LSBs are superframe counter.
1bit FEC(Forward Error Correction)Ind + 1bit reserve + 30bits Super-frame Counter. (4 bytes)
PLOAMd:
carries OAM, ranging, alerts, activation messages, etc. GPON uses PLOAMd as control channel.
1Byte (8bits) ONUid + 1Byte (8bits) message segment + 10Bytes Content body + 1Byte (8bits) CRC checksum bits. (13 Bytes)
Bip:
SONET/SDH-style Bit Interleaved Parity of all bytes since last BIP.(1 Byte)
PLend: (4 Bytes)
Transmitted twice for robustness, including three parts:
Blen – 12 MSB are length of BW map in units of 8 Bytes Alen – Next 12 bits are length of ATM partition in cells CRC – final 8 bits are CRC over Blen and Alen
US BW map:
The array of Blen 8Bytes structures granting BW to US flow, telling in which time segment the ONT should transmit the data.
Each access 8Bytes defines a time message.More detail description is sharing in our blog “Gpon-Epon’s key technologies:DBA & T-CONT ”. (N*8Bytes)
BWmap is sent by OLT to ONUs ,including a list of these fields:
Alloc-id: ONU allocation IDs Flags: Used to indicate the behavior of ONU, such as, next uplink data transmission(PLOAMu,PLSu,DBRu etc). S-start,S-stop:start and stop times (16bits fields, in Bytes from beginning of US frame) CRC:CRC(cyclic redundancy check) Checksum.
VLANs and GEM Ports
Terminology
| AB | Assured Bandwidth | |
| AES | Advanced Encrypt System | |
| AGC | Automatic Gain Control | |
| AN | Access Network | |
| BE | Best-offer Bandwidth | |
| BWmap | bandwidth map | |
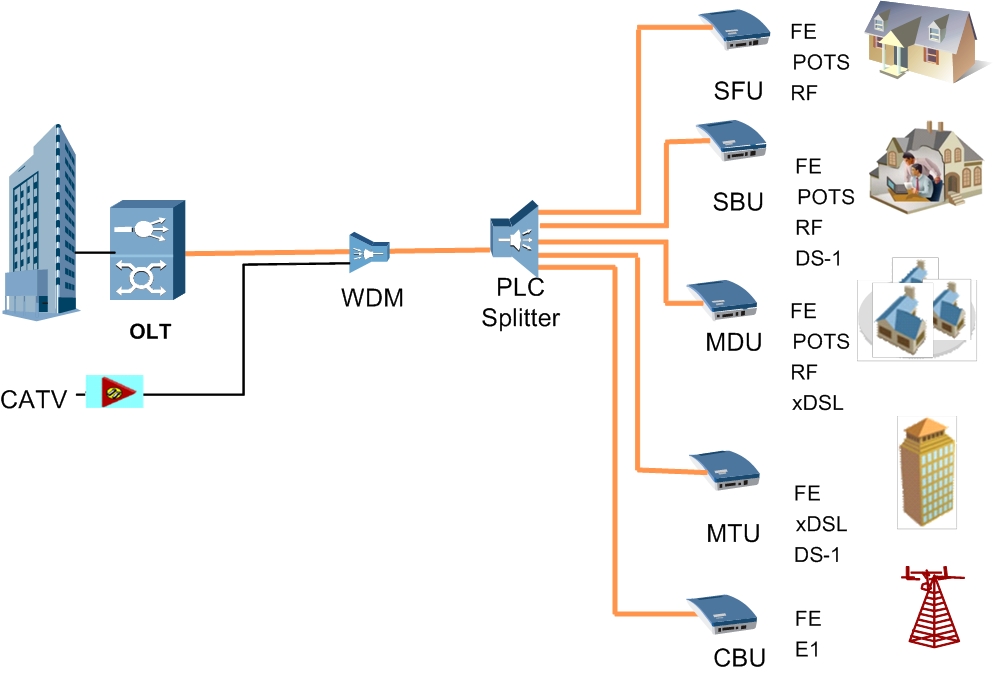
| CBU | Cell Base Unit | |
| DBA | Dynamically Bandwidth Assignment/Allocation | |
| DSLAM | Digital Subscribe Line Access Multiplexer | |
| EFMA | Ethernet in the First Mile Alliance | |
| EPON | Ethernet Passive Optical Network | |
| EqD | Equalization Delay | |
| FB | Fixed Bandwidth | |
| FSAN | Full Service Access Networks | |
| FTTB | Fiber to the Building | |
| FTTC | Fiber to the Curb | |
| FTTH | Fiber to the Home | |
| FTTN | Fiber to the Network | |
| GEM | GPON Encapsulation Method | |
| CID | Consecutive Identical Digit | |
| GPON | Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Network | |
| GTC | transmission convergence | |
| HEC | header error check | |
| JF | Jumbo Frames | |
| MSAN | Multi-service Access Network | |
| MDU | Multi Dwelling Unit | |
| MTU | Multi Tenant Unit) | |
| NAB | Not-assured Bandwidth | |
| NE | Network Element | |
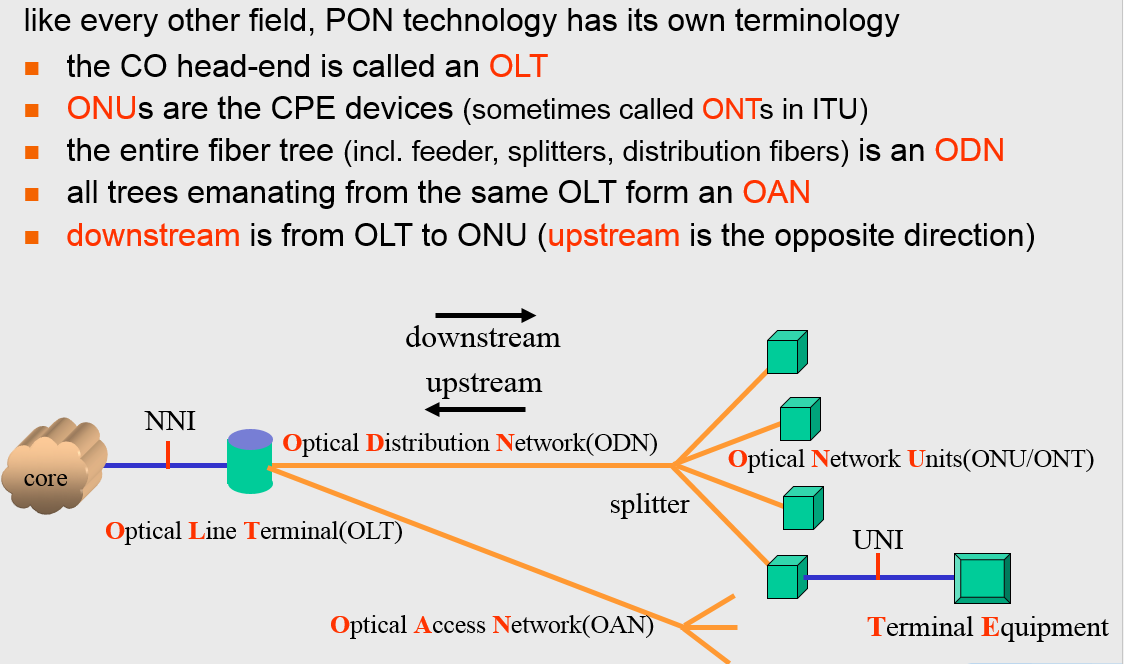
| NNI | network-to-network interface | An NNI circuit can be used for interconnection of signalling (e.g., SS7), Internet Protocol (IP) (e.g., MPLS) or ATM networks. |
| NRZ | Non-return-to-Zero | |
| OAM | Operation, Administration and Maintenance | |
| OCMI | ONU Management and Control Interface. | |
| ODN | Optical Distribution Network | |
| OLT | Optical Line Terminal | |
| OMCI | The ONU management and control interface | |
| ONT | Optical Network Terminal | Almost same with ONU but normally with large port count, like E1/GE |
| ONU | Optical Network Unit | |
| P2P | Point to Point | |
| P2MP | Point to Multi-Point | |
| PCBD | Physical Control Block Downstream | |
| PLI | Payload Length Indicator | |
| PLOAM | Physical layer OAM Operations, Administrations and Maintenance | |
| PON | Passive Optical Network | |
| POS | Passive OpticalSplitter | |
| Port-ID | traffic identifier | Identifies the target ONU |
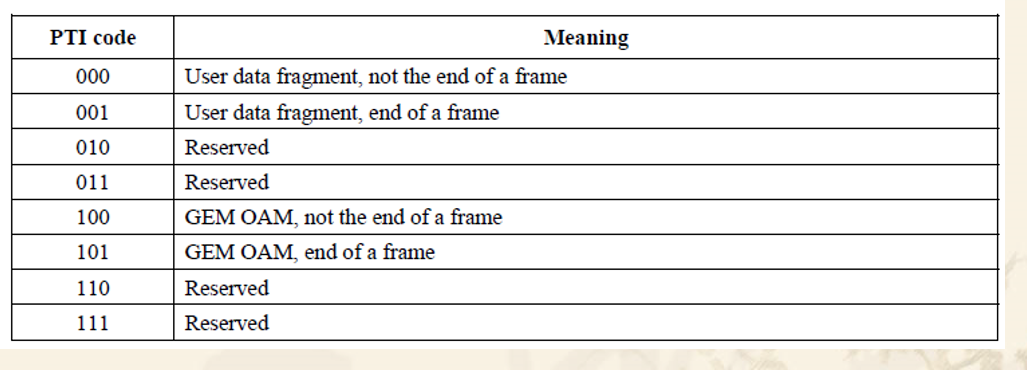
| PTI | payload type indicator | |
| RTD | Round Trip Delay | |
| RTT | Round Trip Time | |
| SerDes | Serializer/Deserializer pronounced sir-deez | |
| SFU | Single Family Unit | |
| SBU | Single Business Unit | |
| SNI | Service Node Interface | |
| TDM | Time Division Multiplexing | |
| TDMA | Time Division Multiple Access | |
| T-CONT | Transmission Containers | |
| UNI | User Network Interface | a demarcation point between the responsibility of the service provider and the responsibility of the subscriber. |
| VoD | Video On Demand | |
| WDM | Wavelength Division Multiplex Module |